Fig. 1.
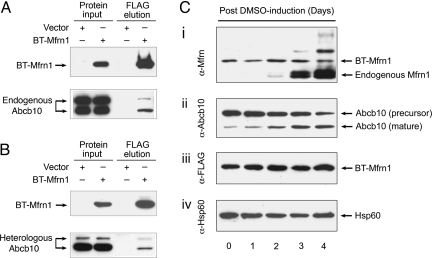
Physical interaction between Mfrn1 and Abcb10 proteins is confirmed in MEL cells and transfected heterologous cells. (A) IP/Western blot analysis of interaction between Mfrn1 and endogenous Abcb10 in differentiated MEL cells stably expressing engineered BT-Mfrn1 or empty vector. (B) IP/Western blot analysis of Mfrn1–Abcb10 interaction from transient transfection of control vector or BT-Mfrn1 in heterologous COS7 cells. Protein input lysate is shown on the respective left columns. Only in the presence of Mfrn1 is Abcb10 selectively copurified from Mfrn1–protein complex. (C) Endogenous Mfrn1 and Abcb10 are induced in chemically differentiated stable MEL cells expressing BT-Mfrn1. Mitochondrial lysates collected from MEL cells exposed to 1.5% DMSO for varying numbers of days were serially probed with antisera against native mouse Mfrn1 (i), antisera against Abcb10 (ii), antisera against FLAG peptide (iii), and antisera against loading control Hsp60 (iv). BT-Mfrn1 protein is constitutively expressed from the EF1α promoter (i and iii), whereas endogenous Mfrn1 is induced during MEL erythroid maturation (i). Abcb10 is proteolytically processed to a mature isoform in MEL cells during erythroid differentiation (ii).