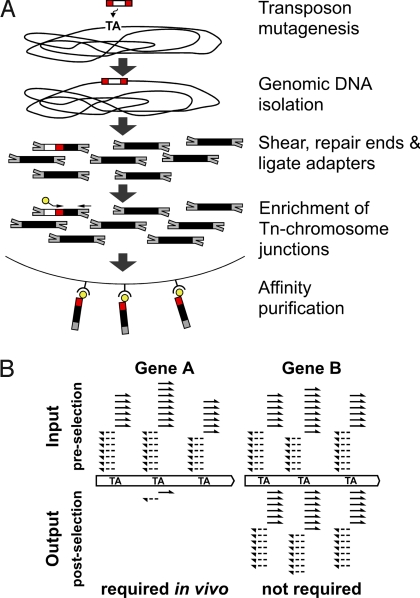
Fig. 1.
HITS and comparison of selected libraries. (A) HITS sample preparation and enrichment of transposon/chromosome junctions. After transposon mutagenesis, chromosomal DNA is purified from H. influenzae mutant library. Red, ITRs of himar1 transposon; white, contents of transposon, including the kanamycin resistance gene. Illumina oligonucleotide adapters (gray) are ligated to sheared genomic DNA. Fragments of the transposon/chromosome junctions are enriched via PCR using transposon- and adapter-specific primers. The biotinylated transposon-specific primer (yellow) anneals to the ITRs of the transposon and includes the Illumina sequencing primer site. The adapter-specific primer anneals to only 1 oligonucleotide of the partially complementary adapter. Enriched fragments are collected using streptavidin-coated paramagnetic beads. After washing, single-stranded DNAs are eluted from the beads and used for cluster formation on Illumina flow cells. (B) Comparison of lung-selected output library to input library. After sequencing, reads are mapped to the reference genome (solid arrows, plus strand; dashed arrows, minus strand) to identify the transposon insertion sites. The number of insertion sites detected per gene and the number of sequencing reads per site are used to determine the relative abundance of the mutant within the library before and after selection. The examples depict insertion patterns at TA sites in hypothetical gene A, in which insertion mutations confer attenuated growth or survival during infection, and gene B that is not required for growth in vitro or in vivo. Insertions in genes that are essential for growth on rich culture media are absent in the input library and are not detected by HITS.