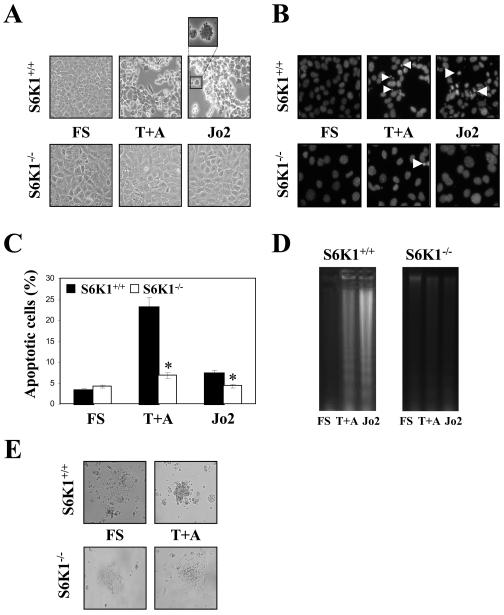
Figure 2. Apoptosis induced by death receptor activation was reverted in S6K1-deficient neonatal hepatocytes.
S6K1+/+ and S6K1−/− immortalized hepatocytes were stimulated with TNFα (30 ng/ml) plus actinomycin D (100 ng/ml) (T+A) or Jo2 (2 μg/ml), for 16 h in DMEM plus 5% FS. A. Representative phase-contrast micrographs of S6K1+/+ and S6K1−/− hepatocytes after apoptotic stimuli. B. Representative images of the nuclear morphology of untreated and treated S6K1+/+ and S6K1−/− hepatocytes after staining of DNA with DAPI and visualization by fluorescence microscopy. C. The percentage of cells with DNA lower than 2C (apoptotic cells) was determined by flow cytometry. Results are means ±SE. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t test comparing the S6K1−/− condition with the respective values for wild-type controls. *p<0.05 was considered significant. D. Extranuclear DNA obtained from untreated and treated S6K1+/+ and S6K1−/− hepatocytes was electrophoresed and visualized by UV fluorescence. A representative experiment is shown. E. Representative phase-contrast micrographs of S6K1+/+ and S6K1−/− primary hepatocytes after exposure to the apoptotic stimuli TNFα (30 ng/ml) plus actinomycin D (100 ng/ml) (T+A) for 16 h.