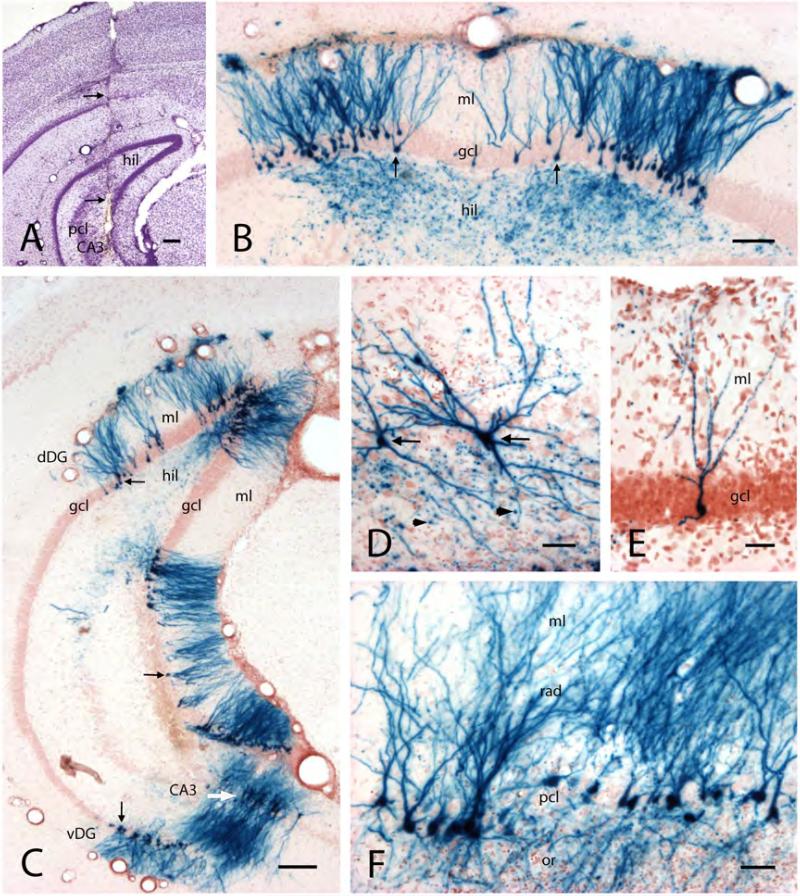
Figure 7. Hippocampal cell infection with HSVI viral vector containing genes for Kv1.1 channel protein and β-galactosidase.
A) Transverse section from the caudal hippocampus, showing the track of a cannula (arrows) used for vector injection. The cannula tip is positioned within hilus (hil) and CA3 pyramidal cell layer (pcl).
B) Transverse section of the dentate gyrus in the dorsal hippocampus, showing β-gal in numerous granule cells (X-Gal histochemical staining, yielding blue cells). Note the complete staining of cell bodies (arrows) in the granule cell layer (gcl), dendrites in the molecular layer (ml), and mossy fiber axons and boutons in the hilus (hil).
C) Low power transverse section from the caudal hippocampus, showing X-Gal-stained granule cells (arrows) and CA3 pyramidal neurons (white arrow) in dorsal (dDG) and ventral (vDG) hippocampal/dentate gyrus regions. Abbrevations: hil, hilus; gcl, granule cell layer; ml, molecular layer.
D) Higher magnification of two representative X-Gal-stained CA3 neurons (arrows). Note the punctate staining around the cells, reflecting X-Gal-stained mossy fiber boutons (arrowheads).
E) Higher magnification of a representative X-Gal-stained granule cell.
F) Transverse section from the ventral hippocampus showing X-Gal-stained CA3 pyramidal neurons. Abbreviations: rad and ml, strata radiatum and moleculare; pcl, pyramidal cell layer; or, s.oriens.
Scale bars: A and C: 200μm; B: 100μm; D and F: 50μm; E: 20μm.