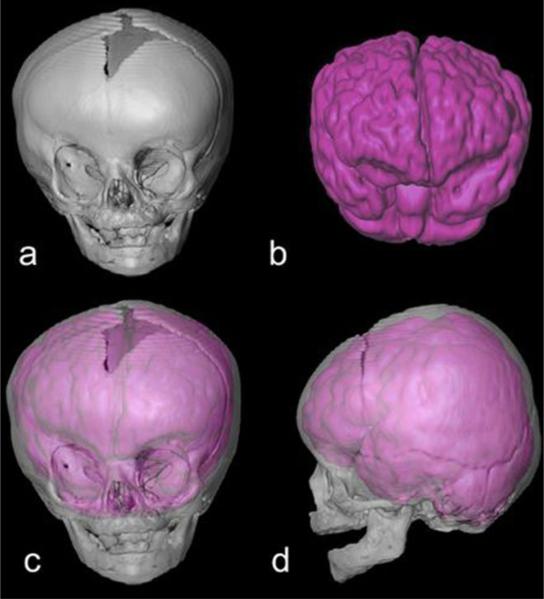
Fig. 1.
3D reconstruction of CT images of the craniofacial skeleton and MR images of the central nervous system of a 21-week-old child with right unilateral synostosis of the coronal suture (RUCS). Features consistent with the diagnosis of RUCS include a flattened frontal bone on the side of the fused suture, and a “twisting” of the facial skeleton and cranial base (not shown). The four panels include: (a) anterior view of 3D reconstruction of skull; (b) anterior view of 3D reconstruction of brain; (c,d) anterior, lateral views of 3D reconstruction of skull superimposed (and ghosted for transparency) over the 3D brain reconstruction to show anatomical relationships of brain and skull. CT and MR images were acquired separately. Consequently, the superimposition used in this figure is based on anatomical knowledge rather than any superimposition or registration algorithm.