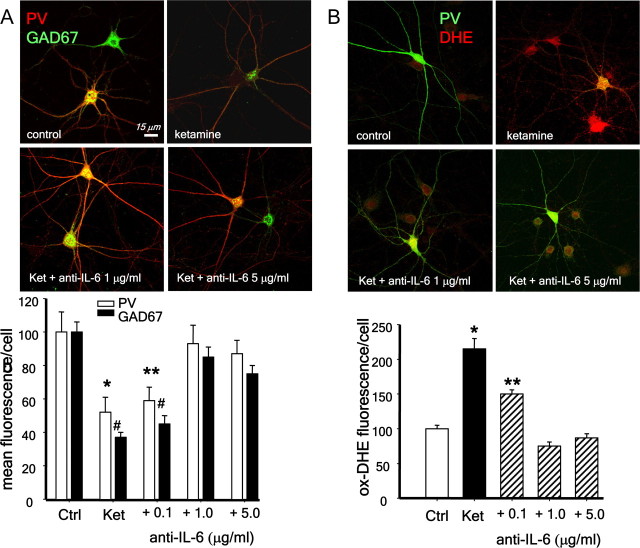
Figure 7.
Blocking IL-6 with antibodies prevents ketamine effects on PV-interneurons. Primary neuronal cultures were exposed to ketamine in the absence of the astrocytic monolayer and in the presence of an anti-mouse IL-6 blocking antibody produced in goat (α-mIL-6). A, Increasing concentrations of α-mIL-6 prevented the decrease in PV and GAD67 after 24 h of ketamine exposure. Bar graph show results for fluorescence quantification of both antigens in PV-interneurons expressed as % of control. *,**p < 0.05; #,## p < 0.001. n = 4 experiments per condition. Baseline intensities: PV = 165 ± 30; GAD67 = 127 ± 28. B, Neuronal cultures were treated as in A, and DHE was added for the last hour of treatment. After fixation, the coverslips were processed for immunocytochemistry for parvalbumin (PV, green). Bar graphs show results for oxidized DHE fluorescence (red) intensity analysis in all neurons including PV-interneurons. (*p < 0.001 compared with control and **p < 0.001 compared with ketamine. n = 3 experiments per condition.) Baseline intensities: DHE = 25.4 ± 5.4.