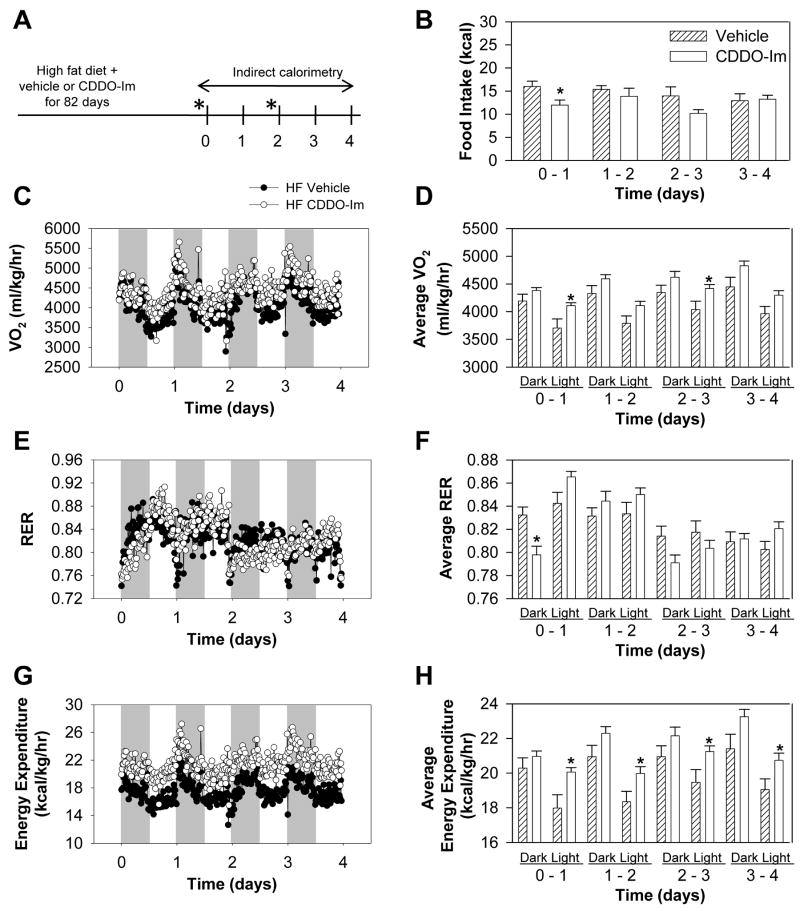
Fig. 2.
Indirect calorimetry and food intake analysis in wild-type mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Protocol for indirect calorimetry. High-fat diet-fed mice were treated with 30 μmol/kg body weight CDDO-Im or vehicle for 82 days and indirect calorimetry was performed thereafter from days 0 to 4. Mice were dosed with CDDO-Im on days 0 and 2 (*). (B–H) All data represent mean ± S.E.M., n = 8 per group. * P < 0.05, CDDO-Im vs. vehicle. (B) Food intake (C) Oxygen consumption (VO2) (D) Average oxygen consumption (E) Respiratory exchange ratio (RER) (F) Average respiratory exchange ratio (G) Energy expenditure normalized to body weight (H) Average energy expenditure normalized to body weight.