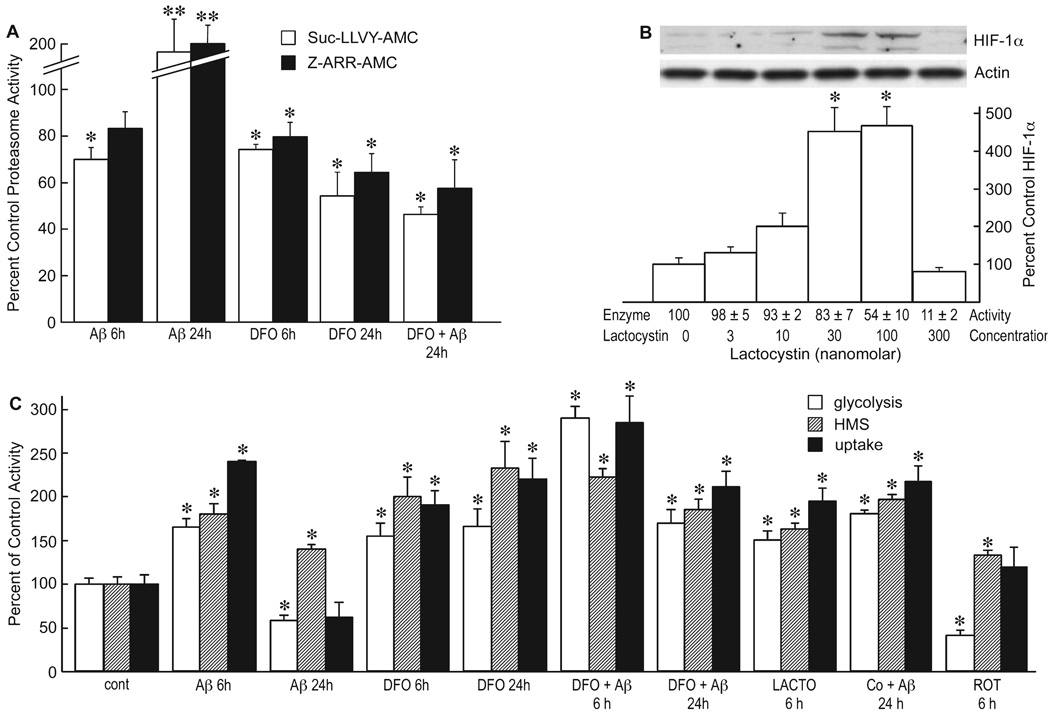
FIG.5.
Amyloid beta peptide (Aβ) inhibits proteasome enzyme activity. (A) Glial cells were treated with 1 µm Aβ1–42 for 6 or 24 h in the presence or absence of 50 µm desferoxamine (DFO) and the proteasome activity of the cells assayed using Suc-LLVY-AMC (chymotrypsin substrate) or Z-ARR-AMC (trypsin substrate). The data are presented as the percent control (vehicle alone) activity *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001 ANOVA (n = 4). (B) Cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of lactacystin, and the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α was monitored by Western blotting and quantified as percent control. Proteasome activity (enzyme activity) was monitored using Z-ARR-AMC and the activity given at the bottom of the figure relative to untreated control *P < 0.001 vs. control, one-way ANOVA (n = 4). (C) Cells were treated with 1 µm Aβ1–42, 50 µm DFO, 30 nM lactacystin (LACTO), 100 µm cobalt, 100 µm PG or 1 µm rotenone (Rot) for the indicated times, and the rate of glycolysis (open bar), hexose monophosphate shunt (HMS) activity (hatched bar) or glucose uptake (solid bar) monitored. *P < 0.05 relative to control values at 6 or 24 h for each assay. One-way ANOVA (n = 3) and Tukey’s post hoc test.