Figure 4. Impaired corneal epithelial wound healing response in Cited2 deficient eyes.
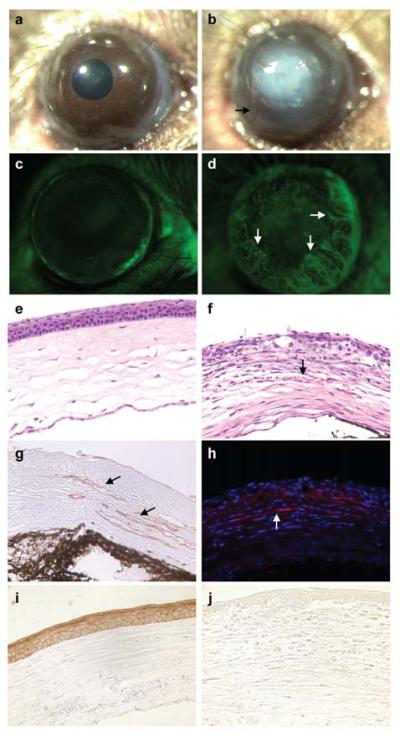
Corneal epithelial debridement was created in the eyes of 6-week old Cited2flox/flox littermate controls and Cited2flox/flox;Le-Cre+ mice. One week after wounding, macroscopic examination showed severe corneal opacification (b) and aberrant corneal neovascularization (arrow in b) in Cited2flox/flox;Le-Cre+ eyes, which is in distinct contrast to the well healed cornea in Cited2flox/flox controls (a). Fluorescein injection was also performed and showed that only the limbus region was fluorescein positive in Cited2flox/flox controls, whereas the Cited2flox/flox;Le-Cre+ eyes showed fluorescein positive vasculature in the cornea (arrows in d). Further histological examination after H&E staining on eye sections revealed vessels containing red blood cells in Cited2flox/flox;Le-Cre+ corneal stroma (arrow in f) compared to the avascular feature of Cited2flox/flox controls (e). The corneal neovascularization in Cited2flox/flox;Le-Cre+ eyes was further confirmed by CD31 immunostaining (g, brown color; arrows) and α-SMA (h, red for α-SMA and blue for DAPI; arrow) immunostaining. K12 immunostaining was performed and abundant K12 expression was detected in healed corneal epithelium in Cited2flox/flox controls (i, brown color); however, K12 expression was barely detected in Cited2flox/flox;Le-Cre+ corneas (j).
