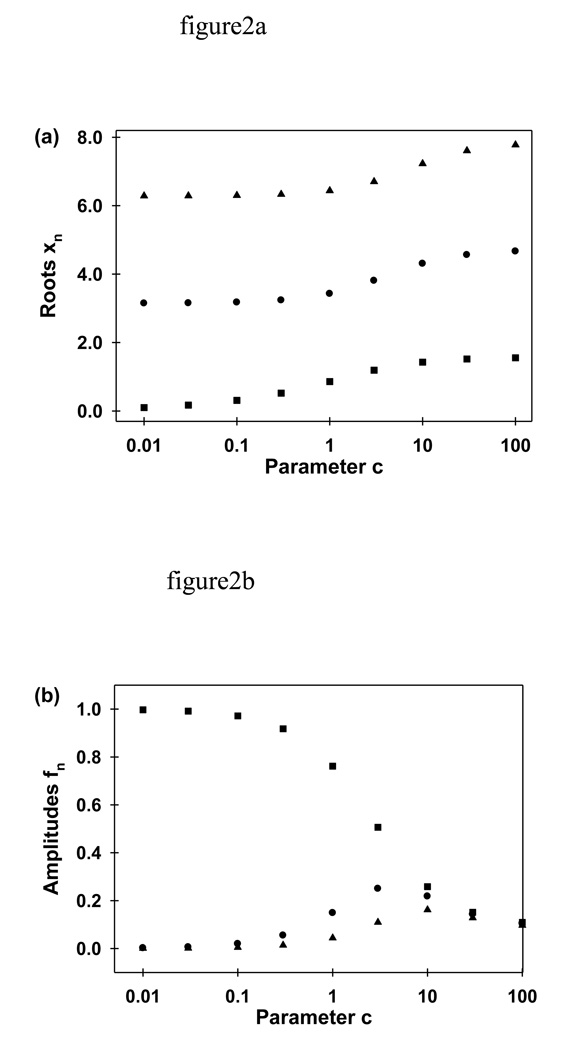
FIGURE 2.
Parameters xn and fn. Fluorescence decay during continuous photobleaching is described by an infinite sum of exponentials with rates D(xn/L)2, where D is the diffusion coefficient and L is the cell length (Eqs. 9 and 19). The parameters xn are a discrete, countably-infinite set of values that are determined by the value of the parameter c. Parameter c depends on experimental conditions (D, L, the depth of the evanescent wave d, and the bleaching propensity κ). Most importantly, c is proportional to the excitation intensity I0. The parameters fn are amplitudes associated with the different exponentially decaying terms and are defined, in general, by the values of c, L, d and xn. (a) The values of x1 (■), x2 (●) and x3 (▲) were calculated numerically as a function of c by using Eq. 9. (b) The values of f1 (■), f2 (●) and f3 (▲) were calculated by using Eq. 19 with L = 2.2 µm and d = 0.1 µm. At low c values, the first amplitude, f1 is much larger than the others and the fluorescence decay can be approximated as a single exponential with rate D(x1/L)2. In addition, for many experimental conditions, the terms associated with rates having n > 1 decay too rapidly to affect the observed fluorescence decay.