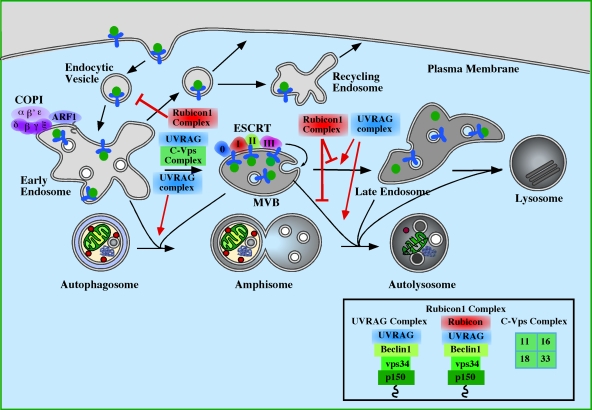
Figure 3.
The role of endosomes and Class III PI3-kinase complexes in autophagosome maturation. Maturation of autophagosomes has been shown to require functional early endosomes, multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and late endosomes. COPI is important for early steps in endocytosis and for autophagosome maturation (Razi et al., 2009). Similarly, the ESCRT complexes participate in autophagosome maturation and later steps of endocytosis (Raiborg and Stenmark, 2009). Loss of either COPI or ESCRT results in the accumulation of autophagosomes and amphisomes. Loss of the Class III PI3K subcomplex p150-Vps34 (see Fig. 2) would also be predicted to have a similar inhibition of maturation as it is required to maintain endosomal function on Rab5- and Rab7-positive endosomes. Of the Class III PI3K complexes, the UVRAG complex, described in Fig. 2 and the Rubicon complex (p150–Vps34–Beclin1–UVRAG–Rubicon) regulate autophagosome maturation (Matsunaga et al., 2009; Zhong et al., 2009). UVRAG, required for endosome function, positively regulates maturation and autophagy, while the association of Rubicon to UVRAG causes an inhibition of autophagic maturation. Note: Rubicon complex also reduces the activity of the Class III PI3K. The composition of the complexes is shown in the box. UVRAG can also associate with the core class C–Vps complex, containing Vps11, 16, 18, and 33, independently of Beclin1, and this interaction accelerates autophagy (Liang et al., 2008), perhaps though stimulation of Rab7 activity.