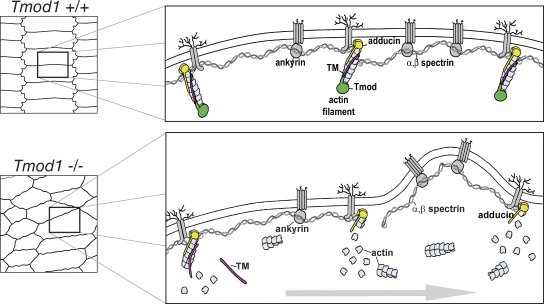
Figure 10.
Molecular mechanism for disruption of the membrane skeleton in the absence of Tmod1. (Top) Model depicting lens fiber cell hexagonal geometry and molecular organization of the membrane skeleton. The short actin filament linkers in the spectrin–actin network are capped by Tmod1 (green) and adducin (yellow) and stabilized by TM (red). The network is linked to membrane proteins via ankyrin (gray ovals), adducin, and 4.1 adaptor proteins (not depicted) (Bennett and Baines, 2001). (Bottom) Model depicting disordered fiber cell packing in lenses lacking Tmod1, due to a hypothetical progression (horizontal gray arrow) of TM dissociation from actin filaments, followed by depolymerization of the short actin filament linkers and disruption of spectrin network connections, leading to membrane instability and abnormal protrusions.