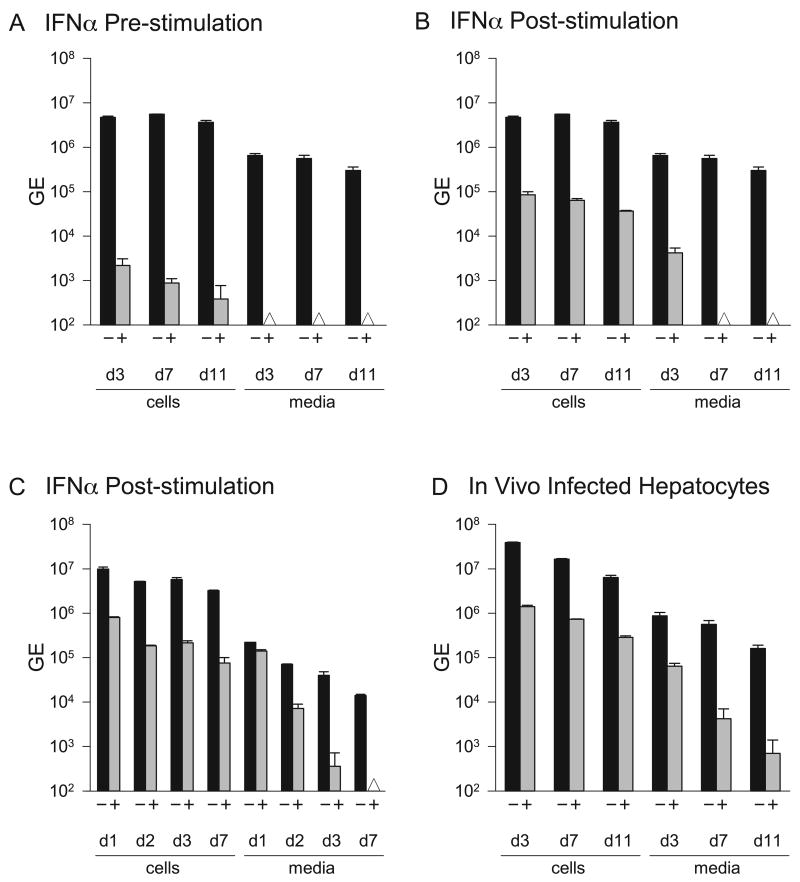
Figure 6.
Time course of antiviral activity of tamarin IFNα2 in GBV-B infected tamarin hepatocytes. A. Pre-infection IFNα treatment. Tamarin hepatocytes were either untreated (-) or treated (+) for 24 hr with 200 ng/ml of tamarin IFNα2 prior to infection with GBV-B, and for an additional 3, 7 or 11 days prior to harvest. B. Post-infection IFNα treatment. Tamarin hepatocytes were infected with GBV-B for 3 days to establish the infection and then treated (+) with 200 ng/ml tamarin IFNα2 for 3, 7 or 11 days before harvest. C. Post-infection IFNα treatment. Tamarin hepatocytes were infected with GBV-B for 3 days prior to treatment (+) with 5 ng/ml of tamarin IFNα2 for 1, 2, 3 or 7 days before harvest. D. Post-infection IFNα treatment. Tamarin hepatocyte cultures were prepared from a tamarin during the acute phase of infection with GBV-B to obtain cells with an in vivo established infection. Three days after plating, the hepatocytes were treated with 200 ng/ml of tamarin IFNα2 for 3, 7 or 11 days before harvest. Black bars = GE of cell-associated GBV-B RNA, grey bars = GE of GBV-B secreted into media. The Δ symbol denotes that the sample was below the level of detection. Error bars indicate the variation in values from duplicate cultures. The level of variation was not sufficient to yield visible error bars on those were none appear.