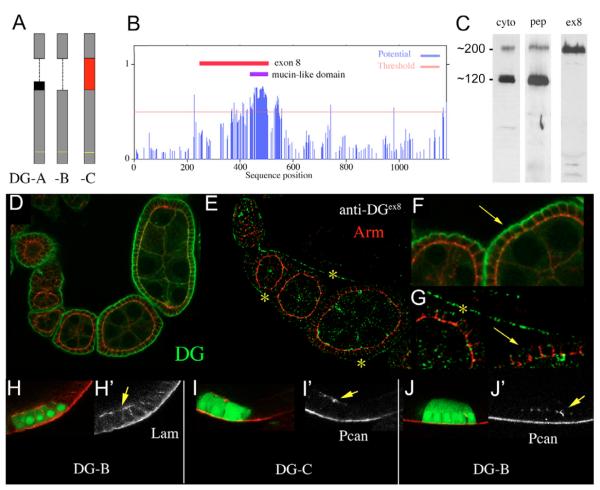
Fig. 5. Perlecan-dependent Dystroglycan lacks the mucin domain.
(A) Schematic drawing of the Dg forms A, B and C, which are generated through differential splicing of exon 8 (red box) and exon 9 (black box). The transmembrane-domain is indicated with a yellow line. (B) Graphic showing the potential of mucin type O- linked glycosylation for each position of the Dg-C sequence. A stretch of 80 amino acids (positions 424-503, indicated by the blue bar) contains a cluster of 52 high potential o-glycosylation sites, which constitute the mucin-like domain. The red bar indicates the region encoded by exon 8 (position 243-507). (C) Western blots of embryonic protein extract (0-20 hours) probed with anti-Dgcyto (cyto), anti-Dgpep (pep) and anti-Dgex8 (ex8). (D-F) Wild-type ovaries stained with anti-Dgcyto (D,F) and anti-Dgex8 (E,G). F and G are higher magnification of D and E, respectively. Dg is strongly concentrated in the basal membrane of the FCE throughout oogenesis (D, arrow in F). Dg-C is expressed in the muscular sheath (yellow asterisks in E and G) but absent from the basal membrane of the FCE (arrow in G). Red, Arm; green, Dg. (H-J) Ectopic expression of Dg-B (H,J) and Dg-C (I) induces ectopic accumulation (arrows) of Lam (H) and Pcan (I,J). Cells expressing the Dg construct are marked by GFP (green). Red indicates Lam (H) and Pcan (I,J). (H’-J’) Red channels only.