Figure 1. Deletion of the cathepsin B gene in transgenic mice expressing human wild-type APP (hAPPwt) reduces brain Aβ40 and Aβ42.
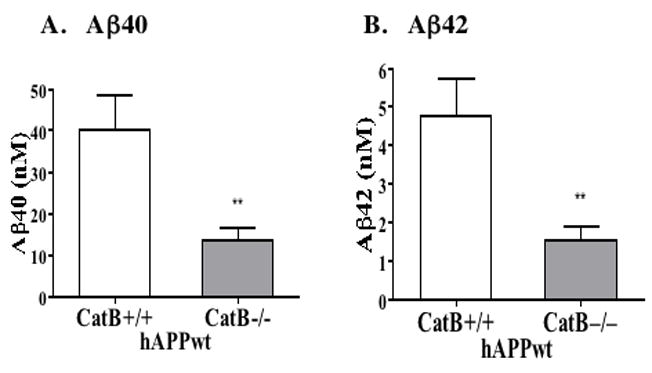
A. Aβ40 levels in brain. The Cat B+/+ and Cat B−/− mice expressing hAPPwt contained mean brain Aβ40 levels of 40.0 ± 21% and 13.6 ± 22% nM, respectively (significant, **p < 0.007). Knockout of the cathepsin B gene resulted in a 66% reduction in brain Aβ40 in mice expressing hAPPwt.
B. Aβ42 levels in brain. The Cat B+/+ and Cat B−/− mice expressing hAPPwt contained mean brain Aβ42 levels of 4.8 ± 21% and 1.5 ± 24% nM, respectively (significant, **p < 0.007). Knockout of the cathepsin B gene resulted in a 68% reduction in brain Aβ42 in animals expressing hAPPwt.
