Fig. 1.
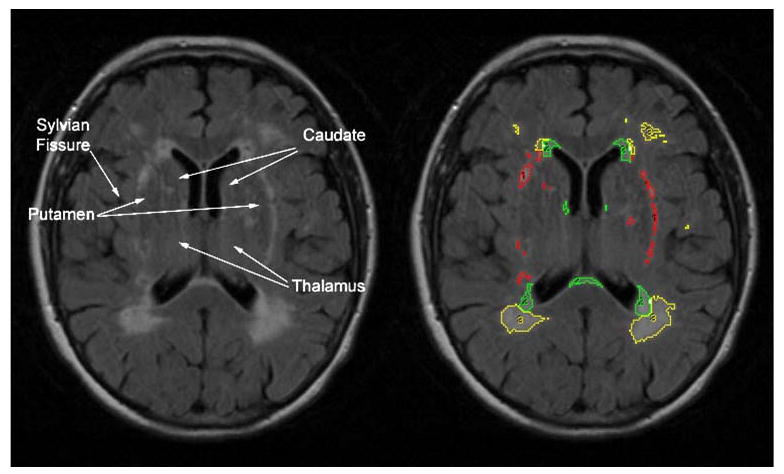
Illustration of MRI method. PERIWMSA were defined as WMSA immediately adjacent to the lateral ventricles within 4 mm. SUBWMSA were defined by the following neuroanatomical boundaries: The superior boundary was defined as the axial slice where the lateral ventricles and the body of the caudate were first visualized; the inferior boundary was defined as the slice where the thalamus and third ventricle were no longer visible; the lateral boundary included the Sylvian fissure and/or the insular cortex; the anterior boundary was the most anterior tip of the lateral ventricles; and the posterior boundary was the most posterior tip of the trigome of the lateral ventricles. DEEPWMSA were defined as those remaining WMSA not included in the aforementioned boundaries containing PERIWMSA or SUBWMSA and were primarily relegated to the corona radiata. Intra- and inter-rater reliability for volume calculation was consistently greater than 0.85 for all WMSA areas. Yellow (3)=DEEPWMSA, green (2)= PERIWMSA, and red (1)=SUBWMSA
