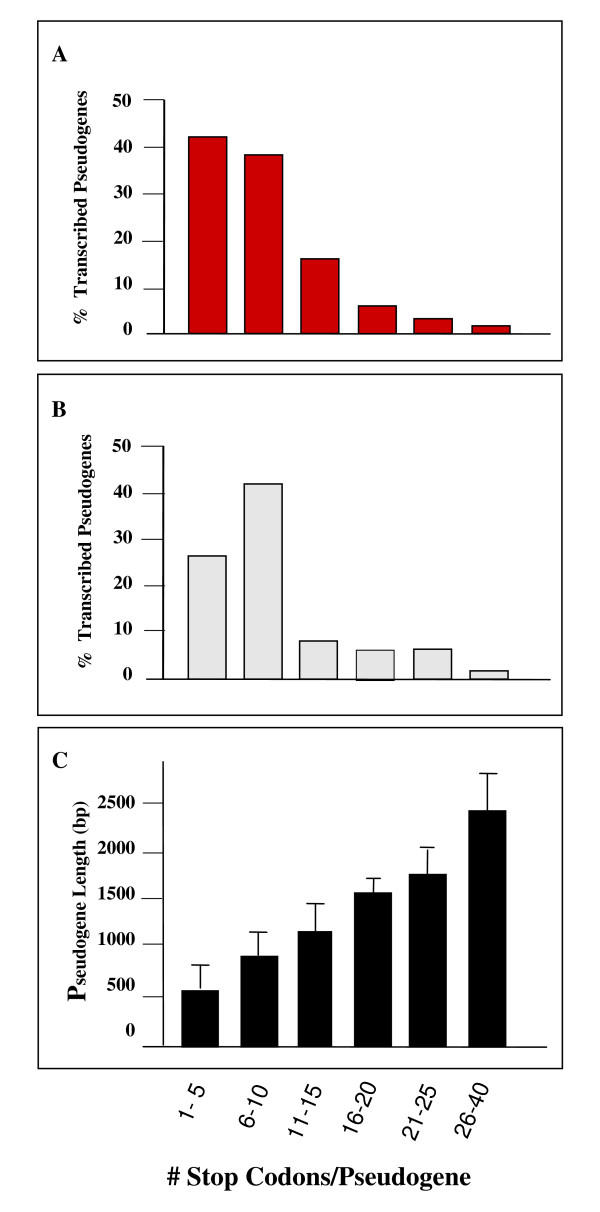
Figure 8.
Translational stop codons within transcribed M. leprae pseudogenes. These graphs show M. leprae transcribed pseudogenes containing translational stop codons (UAA, UGA, or UAG). The number of in-frame (5'3' frame 1) stop codons/pseudogene was identified in silico by translation of the DNA sequence for each pseudogene http://genolist.pasteur.fr/Leproma/. using (ExPasy Translate Tool: http://us.expasy.org/tools/dna.html): Panel A shows the % of transcribed pseudogenes containing the specified number of stop codons/pseudogene (e.g. 1–5, 6–10, etc), obtained by dividing the number of transcribed pseudogenes within each group by that of the total number of transcribed pseudogenes with stop codons; Panel B shows the % transcribed pseudogenes in each group containing translational start codons, obtained by dividing the number of transcribed pseudogenes within each group containing translational start codons by that of the total # pseudogenes with stop codons and translational started codons; Panel C, shows the # of stop codons/group as a function of gene length in base pairs (bp). The mean and standard deviation of the of the gene length (bp) from each group were compared to that of the other groups using GraphPad InStat software and all groups were significantly different (p < 0.001) from all other groups except for 21–25 vs 26–40.