Figure 4. Insulin and LXR regulate Abcg5/ABCG8 expression.
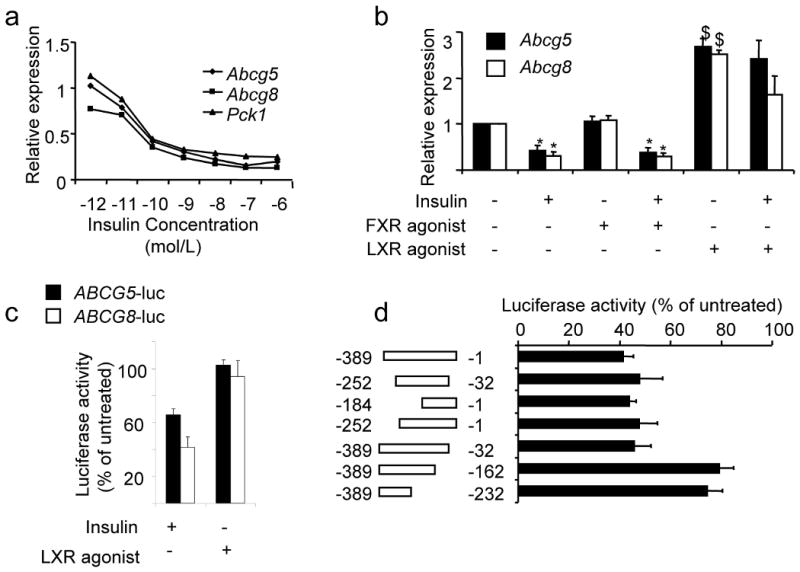
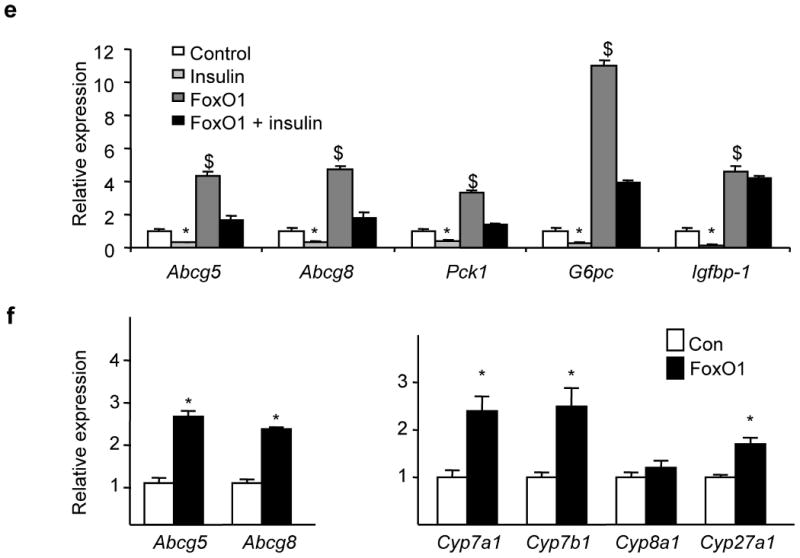
(a) Fao rat hepatoma cells were serum-starved overnight, and then treated with the indicated amounts of insulin for 6-8 hours. We performed real-time PCR and normalized the expression of each gene to its expression level in the absence of insulin (n=3). (b) Cells were cultured overnight in the presence or absence of 100 nM insulin, and either vehicle (DMSO), 50 nM FXR agonist (GW4064) or 5 μM LXR agonist (T090137). Gene expression was measured by real-time PCR analysis (n=3). (c) Cells were transfected with a luciferase reporter fused to the intragenic region of the ABCG5/ABCG8 gene in either the ABCG5 or ABCG8 orientation, and treated overnight with 100 nM insulin or 5 μM LXR agonist, or left untreated (n=3-5). (d) As described in Methods, we made constructs containing deletions in the ABCG5/ABCG8 intragenic region (in the ABCG8 orientation) and tested their ability to respond to insulin. For each construct, data are presented as luciferase activity in the presence of insulin divided by luciferase activity in the absence of insulin x 100% (n=3-8). (e) Cells were infected with control adenovirus or adenovirus encoding constitutively active FOXO1. Two days following infection, cells were washed, and incubated overnight in the presence or absence of 100 nM insulin, before being harvested for real-time PCR analysis (n=3). (f, g) Real-time PCR was used to measure gene expression in 8-week old male mice overexpressing constitutively active FOXO1 under the α1-antitrypsin promoter and their controls, after being fed a high carbohydrate diet for six hours after a 24 hour fast, as described previously 18 (*p<0.05 versus value in the absence of insulin; $p<0.05 versus value in the absence of agonist or constitutively active FOXO1)
