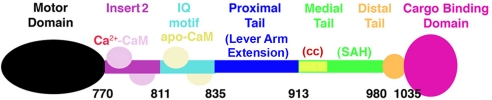
Fig. 1.
Diagram of myosin VI structural domains. Myosin VI contains a motor domain (N terminus), followed by a short lever arm that is composed of a unique insert (insert 2), containing a calmodulin (CaM)-binding site, and an IQ motif that binds a second CaM (3). This short lever arm is followed by a region that has been referred to as the proximal tail (PT) domain, which exists as a folded three-helix bundle in myosin VI monomers and unfolds to for a lever arm extension in dimers (6). This region is followed by the medial tail (MT), which likely has a short segment of weak coiled coil (cc) followed by a stable single α-helix, or SAH (18). This is followed by the distal tail (DT) and finally by the cargo-binding domain (CBD).