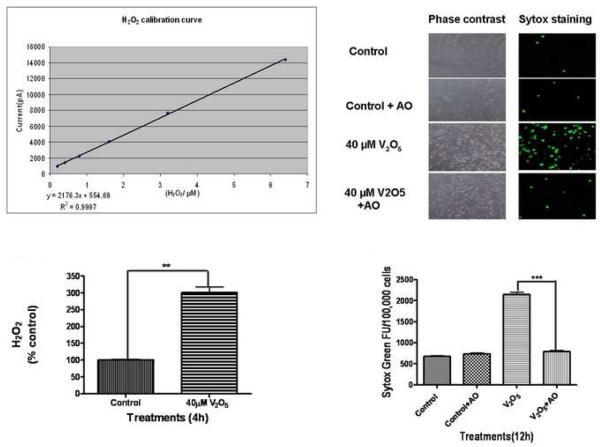
Fig. 3.
Role of oxidative stress in vanadium-induced neurotoxicity in N27 dopaminergic neuronal cells. (A) Calibration curve of H2O2 production by polarography: H2O2 production was measured using an Apollo 4000 Free Radical Analyzer (WPI, Sarasota, FL) equipped with a 100-μm H2O2 sensor. The 100-μm H2O2 sensor probe was calibrated using various doses of H2O2 according to the manufacturer's instructions. The calibration curve was used to calculate the H2O2 in the control and treatment groups. (B) Vanadium induced H2O2 generation in N27 cells. The measurements were conducted in a 96 well plate containing N27 cells exposed to 40 μM vanadium for 4 h. Each measurement was started by insertion of the 100-μm H2O2 sensor probe into wells containing cells. The output signal was recorded and compared to the standard curve. (C) Effect of antioxidants on vanadium-induced neurotoxicity. N27 dopaminergic neuronal cells were co-treated with vanadium and an antioxidant solution cocktail (AO) of vitamin E, glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase. The Sytox green was added to cells and then cells were observed under a Nikon inverted fluorescence microscope. The pictures were captured with a SPOT digital camera (Diagnostic Instruments, Sterling Heights, MI). (D) Quantitative analysis of the protective effect of AO on vanadium-induced neurotoxicity was measured by the Sytox green cytotoxicity fluorescence assay. Data represent results from four individual measurements and are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. **p<0.001 and ***p<0.01.