Table 1.
Structure, cytototoxicity, and in vitro inhibitory bioactivity of compounds 1–13 against Trypanosoma brucei and Pneumocystis carinii
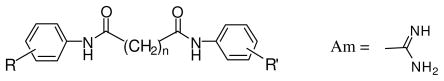 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM)a |
|||||||
| Cpd. # | n | R | R′ | T.b. bruceib | T.b. rhodesiensec | P. cariniid | Cytotox. A549e |
| 1 | 2 | p-Am | p-Am | 9.0 | 2.19 | 0.442 | >44.2 |
| 2 | 3 | p-Am | p-Am | 0.009 | 0.096 | 0.003f | 2276 |
| 3 | 3 | p-CN | p-CN | 6.50 | 7.90 | NTg | NT |
| 4 | 4 | p-Am | p-Am | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002f | 1193 |
| 5 | 4 | p-CO-NH2 | p-CO-NH2 | 2.80 | 1.10 | >100 | NT |
| 6 | 4 | m-Am | m-Am | 0.041 | 0.021 | 33.7 | NT |
| 7 | 4 | m-CO-NH2 | m-CO-NH2 | NT | 1.97 | >100 | >261 |
| 8 | 4 | p-Am | m-Am | 0.012 | 0.007 | 2.27 | >227 |
| 9 | 5 | p-Am | p-Am | 0.002 | 0.002 | 2.37 | >237 |
| 10 | 6 | p-Am | p-Am | 0.003 | 0.001 | 1.95 | 176 |
| 11 | 7 | p-Am | p-Am | 0.400 | 0.240 | 2.44 | 2.87 |
| 12 | 8 | p-Am | p-Am | 0.002 | 0.004 | 4.28 | 249 |
| 13 | 10 | p-Am | p-Am | 0.008 | 0.007 | 3.07 | 18 |
| Pentamidine | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.50f | 24.0f | |||
Each value is the average of at least two determinations.
The Trypanosoma brucei brucei strain was Lab 110 and the Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense strain was KETRI 243 (see refs 16 and 17).
Pneumocytis carinii was obtained from rat lungs (see ref 18).
Cytotoxicity with A549 epithelial lung cell monolayers from human carcinoma (see ref 18).
Data obtained from reference 15.
NT, Not tested.
