Figure 3.
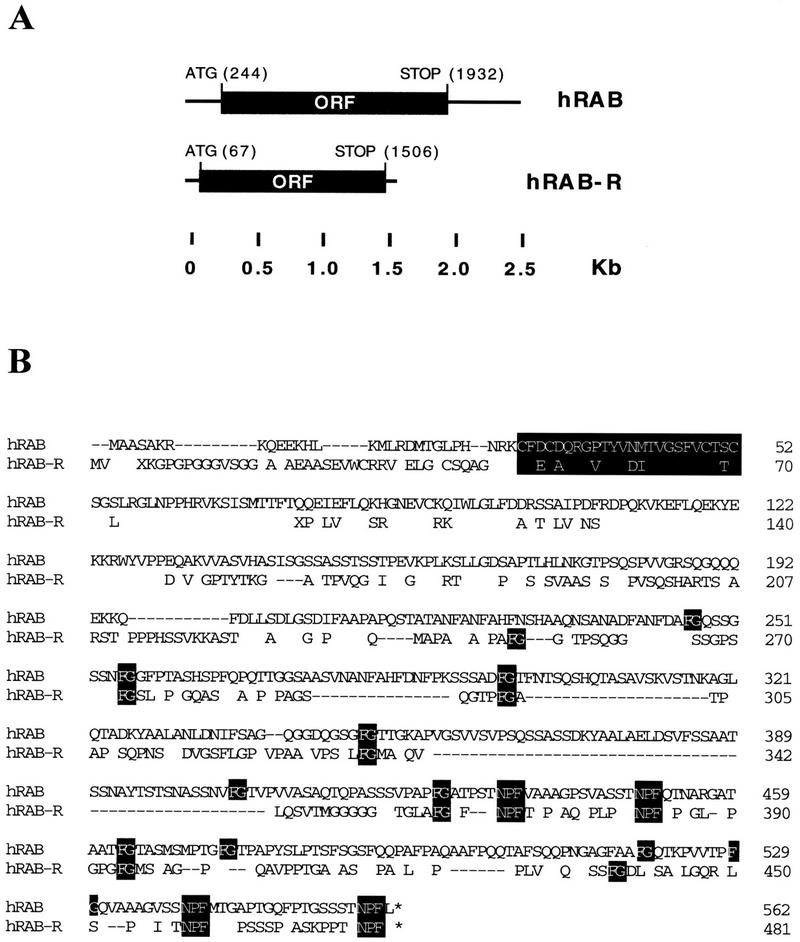
Human RAB and RAB-R cDNAs and proteins. (A) The structures of the human RAB (hRAB) and RAB-R (hRAB-R) cDNAs are depicted. The ORFs are labeled. Positions are indicated in kb. The nucleotide positions of initatior and terminator codons are also indicated. Canonical polyadenylation sites (AATAAA) are at positions 2499, 2542, and 2556 of the RAB sequence; no polyadenylation site was found in the isolated hRAB-R cDNA (not shown). (B) Predicted protein sequences and alignment of human RAB and RAB-R. The sequence of hRAB is identical to that reported by Bogerd et al. (1995) and Fritz et al. (1995). In the hRAB-R sequence, only nonidentical amino acids are reported, except for the FG and NPF motifs. Dashes indicate gaps introduced to maximize the alignment. Accepted conservation, employed to calculate relatedness, are D, E, N, Q; L, I, V, M; K, R, H; F, Y, W; and A, G, P, S, T. The FG, zinc-finger, and NPF motifs are indicated in reverse print.
