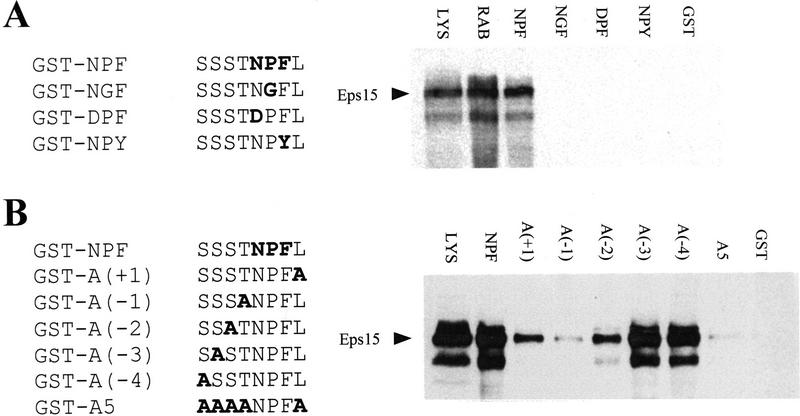
Figure 6.
Requirement for the NPF motif and surrounding positions for binding to Eps15. (A) Binding to Eps15 of mutant peptides containing mutations in the NPF sequence. Peptides engineered in GST fusion proteins are indicated on the left. GST–NPF corresponds to the sequence of a NPF-containing peptide derived from the sequence of RAB (underlined in Fig. 1C). Mutant peptides (GST–NGF, GST–DPF, GST–NPY) are also indicated. The in vitro bindings to Eps15, obtained as described in Fig. 4, are shown on the right. The lane marked RAB represents an in vitro binding obtained with the GST–RAB protein (Fig. 4A) to serve as a positive control. (B) Alanine scanning. Positions surrounding the NPF motif in the RAB peptide were alanine scanned as indicated on the left. The in vitro binding to Eps15, obtained as described in Fig. 4, are shown on the right. Lanes marked LYS were loaded with 50 μg of total cellular proteins to serve as a reference for the position of Eps15 (also indicated). Amino acids corresponding to mutagenized codons are shown in boldface type.