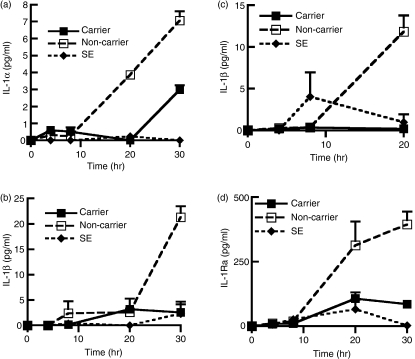
Figure 1.
Nasal epithelial cells (NEC) express reduced levels of interleukin-1α (IL-1α), IL-1β and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) when infected with the nasal carrier strain of Staphylococcus aureus. The NEC layers were cultured at the air–liquid interphase in an antibiotic-free medium and inoculated with 3 × 103 ± 342 (mean ± SEM) colony forming units (CFU) per layer of NEC for a period of up to 30 hr. The organisms used were S. aureus, the carrier strain (D30), the non-carrier strain (930918-3); and S. epidermidis (SE). Levels of (a) IL-1α (b) IL-1β were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay from the apical surface of the NEC. Levels of (c) IL-1β and (d) IL-1Ra were assessed from the basolateral cell culture supernatant. The results represent mean ± SEM of three or four separate experiments.