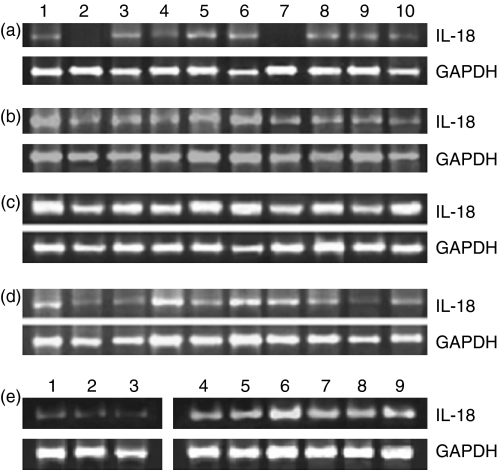
Figure 3.
Interleukin (IL)-18 mRNA expression is up-regulated in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of cirrhotic patients and in the livers of patients with chronic hepatitis C. The gene expression of IL-18 was studied using semiquantitative reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) which yielded products of 342 bp for IL-18 (upper panel) and 983 bp for GAPDH (lower panel). The densitometric assessment was performed using scion image analysis software and the results are expressed as the ratio of IL-18:GAPDH mRNA in PBMC of (a) subjects with resolved hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, (b) chronic hepatitis C patients, (c) patients with HCV-related cirrhosis, and (d) normal healthy controls. IL-18 mRNA expression in the PBMC of cirrhotic patients was significantly up-regulated compared with that in the resolved (P< 0·001), chronic hepatitis (P< 0·01) and control groups (P< 0·001). (e) The patients with chronic hepatitis C (lanes 4–9) expressed significantly higher levels of IL-18 transcripts in the liver (P< 0·025) compared with the controls (lanes 1–3).