Fig. 1. Schematic of the ceramide's mechanism of action in antinociceptive tolerance.
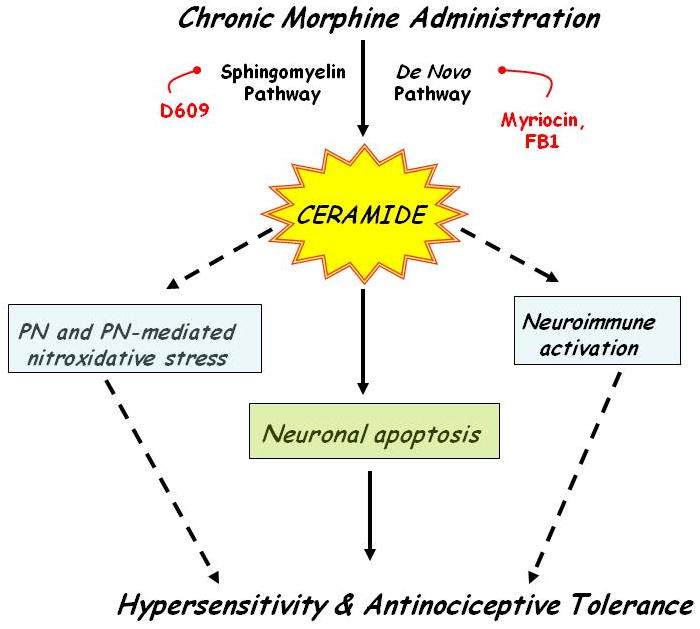
Chronic administration of morphine leads to increased formation of ceramide via the de novo and SMase pathways leading to antinociceptive tolerance; this is blocked by inhibitors of ceramide biosynthesis (this study and [28]). Ceramide fosters the development of tolerance at least in part by neuroimmune activation, formation of PN, PN-mediated inactivation of MnSOD [28] and neuronal apopotosis.
