Fig. 3. Ceramide synthesis was necessary for the development of oxidative DNA damage and PARP activation.
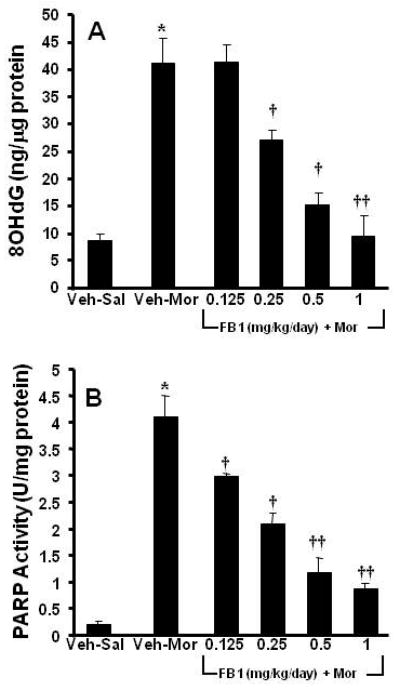
When compared to Veh-Sal, chronic administration of morphine (Veh-Mor) led to oxidative DNA damage as evidenced by a significant increase in 8OHdG (A) and a substantial activation of PARP (B). These events were blocked in a dose-dependent manner by co-administration of morphine with FB1 (0.25-1 mg/kg/d, n=10) (A, B). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM for n=10 animals. * P<0.01 for Veh-Mor versus Veh-Sal; †P<0.01 and ††P<0.001 for FB1-Mor versus Veh-Mor.
