Fig. 4. Biochemical indices of spinal cord apoptosis were dependent on ceramide synthesis.
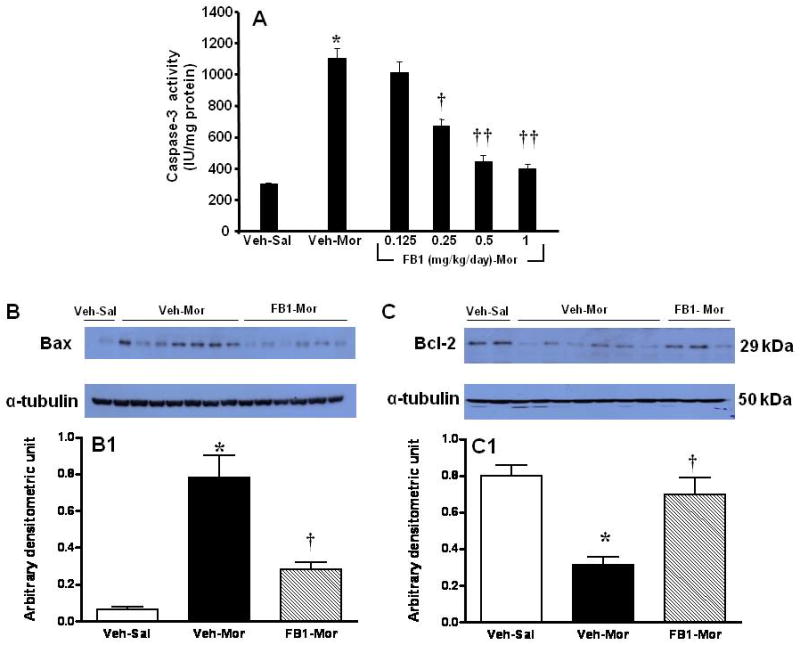
When compared to Veh-Sal, chronic administration of morphine (Veh-Mor) increased the activity of caspase-3 (A) in dorsal horn tissues which was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by FB1 (n=10). Furthermore, chronic administration of morphine increased Bax (B,B1) and concomitantly decreased Bcl-2 (C,C1) as determined by Western blot in dorsal horn tissues. These events were blocked by FB1 (1 mg/kg/d; B,B1,C,C1). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM for n=5 (B1,C1) and n=10 (A) animals. * P<0.01 for Veh-Mor versus Veh-Sal; †P<0.01 and ††P<0.001 for FB1-Mor versus Veh-Mor.
