Fig. 6. TRPV4 channel mediates cyclic strain-induced CE cell reorientation.
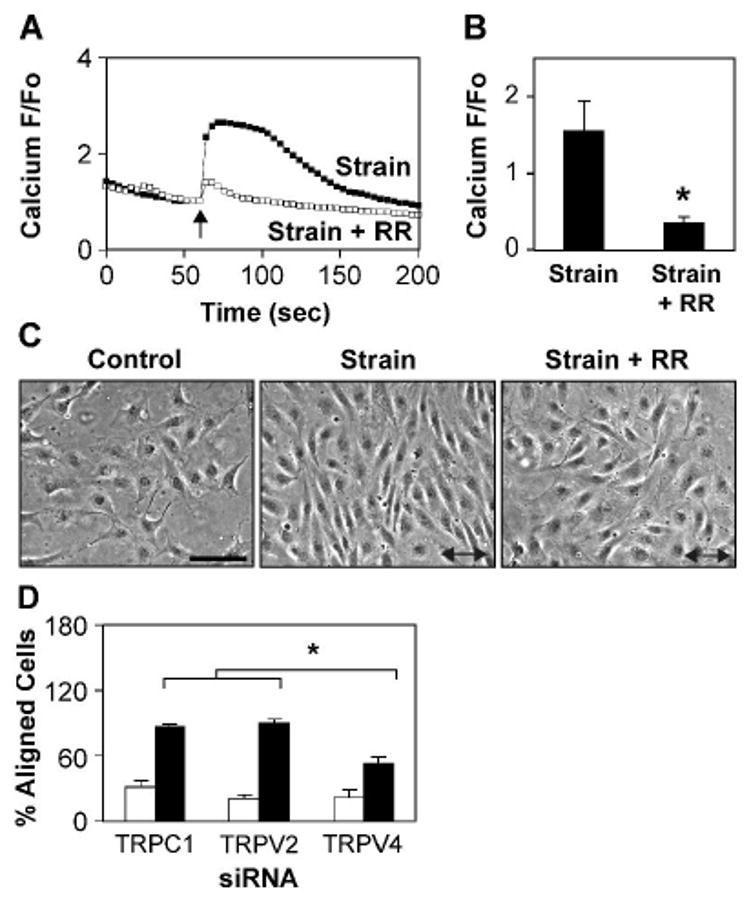
A-B) Relative changes in cytosolic calcium in Fluo-4 loaded CE cells in response to static stretch (15%, 4 sec, arrow) in the absence (■) and presence (□) of the TRPV inhibitor ruthenium red (RR) (*, p < 0.02). C) Phase contrast photomicrographs of CE cells showing the effects of cyclic strain on cell reorientation in the absence and presence of ruthenium red. Arrow indicates the direction of applied strain. Note that ruthenium red inhibits cyclic strain-induced cell reorientation. Scale bar: 50 ·m. D) Percentage of cells oriented 90 ± 30 ° degrees (aligned) relative to the direction of applied strain in control (white bars) and strain exposed (black bars) human CE cells treated with the indicated siRNA. Note that TRPV4 siRNA treated cells failed to reorient fully compared to TRPV2 or TRPC1 treated cells (*, p < 0.0025).
