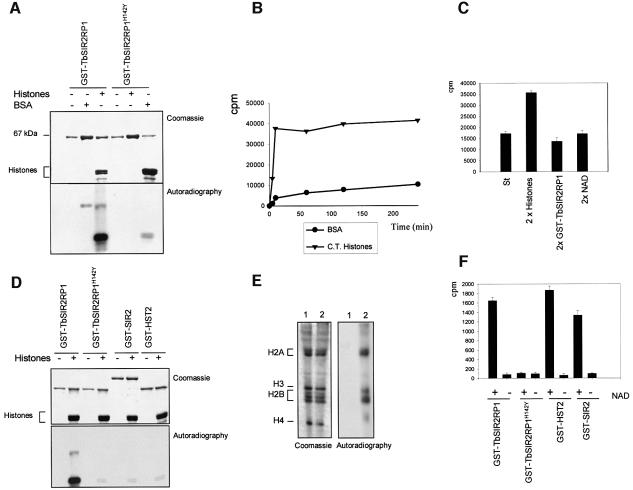
Fig. 3. NAD-dependent ribosylation and deacetylation of proteins by TbSIR2RP1. (A) In vitro ribosylation reactions were performed with 1 µg of GST–TbSIR2RP1 or GST–TbSIR2RP1H142Y, plus 5 µg of BSA and 5 µg of histones using [32P]NAD as donor. The top panel illustrates a Coomassie-stained gel of reaction products resolved by 10% SDS–PAGE, whereas the bottom panel shows the autoradiograph of the gel. (B) Time curves of histone and BSA ribosylation by GST–TbSIR2RP1 at 37°C. Each point represents the ribosylation products of 5 µg of substrate by 0.5 µg of GST–TbSIR2RP1 using 5 µCi of [32P]NAD at the indicated time. Reaction products were precipitated with 20% TCA (w/v), collected and washed on a GF/C glass fibre filter (Whatman), and then counted after addition of liquid scintillation fluid. (C) Ribosylation reactions were performed with 5 µg of histones, 0.5 µg of GST–TbSIR2RP1 and 5 µCi of [32P]NAD (standard reaction, column St) or a double concentration of histone (10 µg, column 2× histones), GST–TbSIR2RP1 (1 µg, column 2× GST–TbSIR2RP1) and [32P]NAD (10 µCi, column 2× NAD). (D) Comparison of TbSIR2RP1 ribosylation activity with that of other members of the SIR2-like family. Ribosylation reactions with 1 µg of GST–TbSIR2RP1, GST–TbSIR2RP1H142Y, GST–SIR2 or GST–HST2 were performed with and without 5 µg of histones using [32P]NAD as donor. The top panel illustrates a Coomassie-stained gel of the reaction products, and the bottom panel shows the autoradiograph of the gel. (E) Triton–acid–urea (TAU) gel of T.brucei histones treated with GST–TbSIR2RP1 or GST–TbHST1H142Y and [32P]NAD, respectively stained with Coomassie blue and autoradiographed. The histone types are indicated on the left. (F) Analysis of the NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity. Histones were acetylated with [3H]acetyl-CoA by HAT1 and then treated with GST–TbSIR2RP1, GST– TbSIR2RP1H142Y, GST–HST2 and GST–SIR2. The amount of acetate released was measured in the presence or absence of NAD.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.