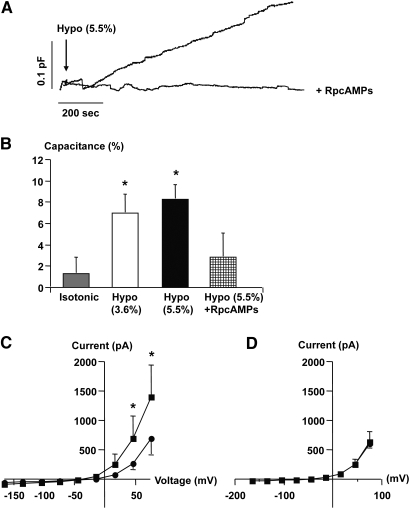
Figure 1.
Effect of hypotonic extracellular fluid on cell capacitance (Cm) changes in single rat JG cells. (A) Traces were obtained in single JG cells and show the effect of exposure to hypotonic fluid (arrow, −) on Cm without and with concomitant dialysis with a PKA inhibitor, RpcAMPs (+, 5 μmol/L). (B) The columns display average changes of Cm in response to hypotonic stimuli (Hypo) with and without intracellular RpcAMPs ± SEM. *P ≤ 0.05 at t = 0 versus t = 10 min. Isotonic: n = 10, Hypo: 3.6%, n = 5; 5.5%, n = 8; Hypo and RpcAMPs: n = 4. (C) The average [current-voltage (I-V)] relationship was determined immediately after the whole-cell configuration was obtained (filled circles). The measurement was repeated 10 min after introduction of a hypotonic stimulus (filled squares). *P ≤ 0.05 at t = 0 versus t = 10 min. (D) Average (I-V) relationship in JG cells measured immediately after the whole-cell configuration was obtained and after 10 min with RpcAMPs.