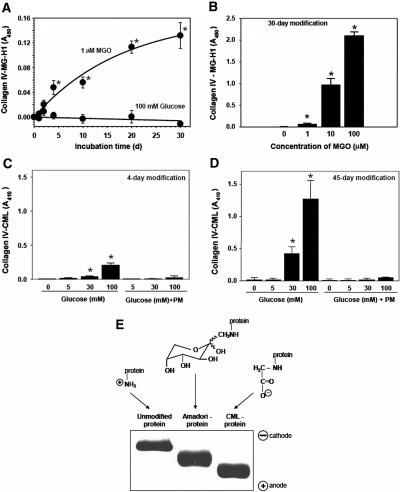
Figure 2.
Modification of collagen IV by MGO or glucose and electrophoretic mobility of glucose-modified albumin. Collagen-IV-coated 96-well plates were incubated (A) with either 1 μM MGO or 100 mM d-glucose, (B) with different concentrations of MGO, (C) d-glucose, or (D) d-glucose and 20 mM PM in 200 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.5 at 37°C. Plates were washed and either MG-H1 or CML modification of collagen IV was determined by ELISA as described in the Concise Methods section. In all figures, data are shown as a mean ± SD (n = 4). *P < 0.05, MGO versus no MGO or glucose versus no glucose. (E) Modified albumin was prepared as described in the Concise Methods section and subjected to nondenaturing PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. The scheme shows the ε-amino group of lysine and its modifications by glycation and glycoxidation reactions in the corresponding samples; the theoretical electrostatic charge of each group at physiologic pH is also shown. Amadori intermediate is depicted in the most prevalent pyranose configuration.