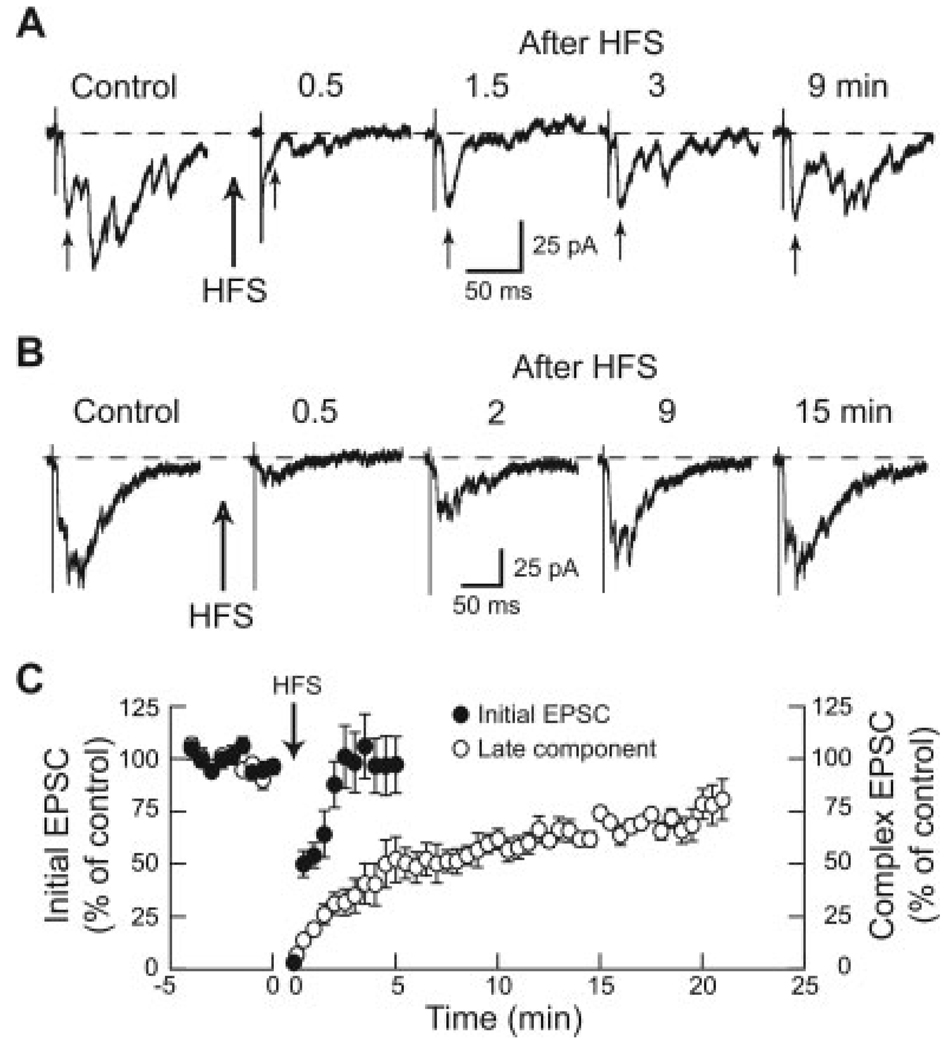
Fig. 3. Early and late components of complex EPSCs recover at different rates following HFS of the STN at 100 Hz for 1 min.
A: Current traces of a complex EPSC that has a clearly recognizable initial EPSC as indicated by small arrows below each trace. Note that the initial EPSC recovers from HFS more quickly than does the late component of the complex EPSC. B: Current traces showing recovery of the late component of a complex EPSC following HFS. In this example, the initial EPSC is not clearly seen. Note that the late component of the complex EPSC requires 15 min to recover fully from HFS. C: Averaged data showing the time courses for recovery of initial (n = 6) and late (n = 12) components of complex EPSCs. Note that the early component recovers within 2 min after stopping HFS, whereas the late component of complex EPSCs requires more than 20 min for full recovery. Initial EPSCs were measured as amplitudes, whereas late components were measured as the integrated area of complex EPSCs.