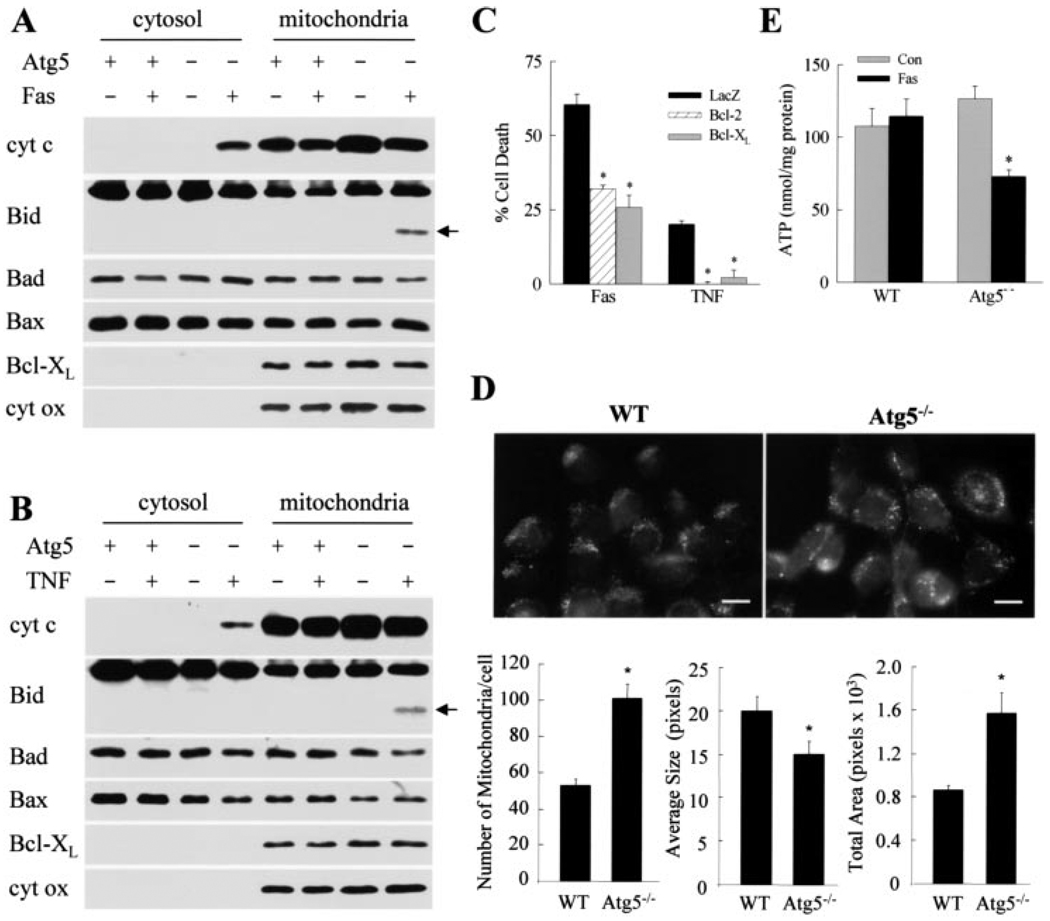
FIGURE 3. Mitochondrial death pathway activation is increased in Atg5−/− cells after death receptor stimulation.
Cytosolic and mitochondrial proteins were isolated from wild-type (Atg5+) and Atg5−/− (Atg5−) cells that were untreated or treated with Jo2 (Fas) (A) or TNF-α (B) and immunoblotted with antibodies for cytochrome c (cyt c), Bid, Bad, Bax, or Bcl-XL. Stripped membranes were reprobed for cytochrome oxidase. Bid cleavage product is indicated by an arrow. C, Atg5−/− cells were infected with adenoviruses that express β-galactosidase (LacZ), Bcl-2, or Bcl-XL. Cells were then treated with Jo2 (Fas) or TNF-α, and the percentage of cell death was determined at 24 h by MTT assay. Data are from 4 independent experiments (*, p < 0.0002). Untreated, wild-type (WT) and knock-out MEFs were stained with Mito Tracker to highlight mitochondria. Top, representative field (bar: 10µm). Bottom, number of mitochondria per cell, average mitochondrial size, and the total cellular area occupied by mitochondria were quantitated. Values are the means of 6–8 fields such as the ones shown (*, p < 0.01 as compared with wild-type cells). E, ATP levels in wild-type and knock-out MEFs untreated (Con) and treated with Jo2 (Fas) for 24 h. Results are from 4 independent experiments (*, p < 0.001 as compared with control cells).