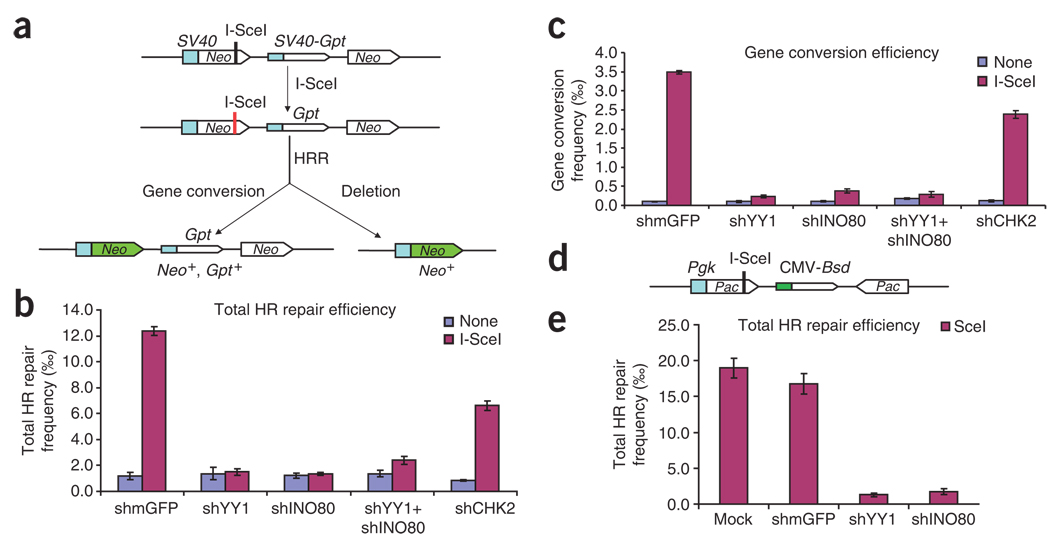
Figure 5.
Impaired homology-directed repair of a chromosomal DSB in YY1- and INO80-deficient 293T and HT-1080 cell lines. (a) Schematic showing how, in the Neo direct-repeat substrate, I-SceI–induced DSBs can result in gene-conversion or deletion products. Neo direct repeats of 1.4 kilobases (open boxes) flank the Gpt gene. Transcription of the upstream Neo is driven by the TEAD1 (here called SV40) promoter and an I-SceI recognition site interrupts the reading frame, whereas the downstream Neo lacks a promoter. Shaded box, SV40 promoter; green arrow, functional Neo gene after repair. (b) Plasmid expressing shRNA constructs was cotransfected with I-SceI plasmid or control plasmid (SceI− plasmid; ‘None’ in key) into HR-293T cells. Total HRR frequencies were calculated as the number of G418-resistant colonies per viable cell plated in selective medium. Blue bars, spontaneous homologous recombination events; purple bars, I-SceI–induced events. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (c) Gene-conversion frequencies, calculated as the number of colonies resistant to both G418 and mycophenolic acid per viable cell plated. (d) Structure of inverted puromycin (Pac) repeats flanking the cytomegalovirus (CMV) Bsd promoter in the HT1080–1885 cell line. The upstream Pac is driven by the mouse Pgk promoter and inactivated by insertion of an I-SceI site in the coding sequence; the downstream donor Pac lacks a promoter. (e) Total HRR frequencies in Pac inverted-repeat HT1080–1885 strain. shRNA constructs were cotransfected with I-SceI plasmid or control plasmid into HT1080–1885 cells. Total HRR frequencies were calculated as the number of puromycin-resistant colonies per viable cell plated in selective medium. Error bars indicate s.e.m.