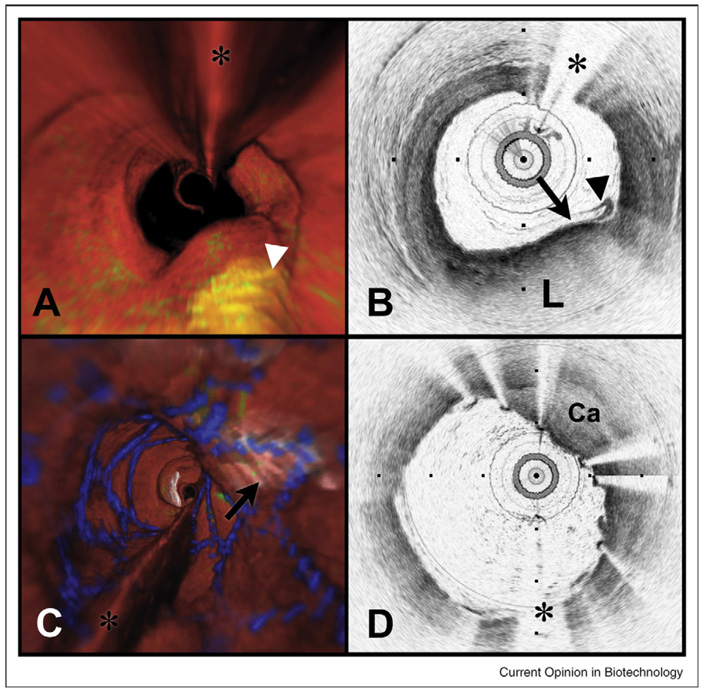
Figure 2.
Volumetric OFDI imaging of the human LAD coronary artery, obtained in vivo. (A) Fly-through rendering view (proximal-distal) of the OFDI dataset, acquired during a single purge of Lactated Ringers solution (3 ml/s), an imaging catheter pullback rate of 2.0 cm/s and at an image acquisition rate of 100 frames per second. The fly-through depicts a yellow, elevated lipid-rich lesion with scattered macrophages (green). (B) OFDI cross-sectional image obtained at the location of the white arrowhead in (A) demonstrates OFDI evidence of a thin-capped fibroatheroma, a lipid pool (L), a thin cap (black arrow), and a dense band of macrophages at the cap-lipid pool interface. A thin flap of tissue (black arrowhead) can be seen over the cap. (C) Fly-through view (proximal to distal) shows a calcified lesion (black arrow) beneath a newly deployed stent. (D) OFDI cross-sectional image obtained at the location of the black arrow in (C) demonstrates a large calcific nodule (Ca) from 11–5 o’clock causing significant stent distortion, highlighted by the shorter inter-strut distances of the overlying stent compared to the opposing vessel wall. Color scale for (A) and (C): red—artery wall; green—macrophages; yellow—lipid pool; blue—stent. Tick marks, 1 mm. (*) Denotes guide wire artifact.