Figure 1.
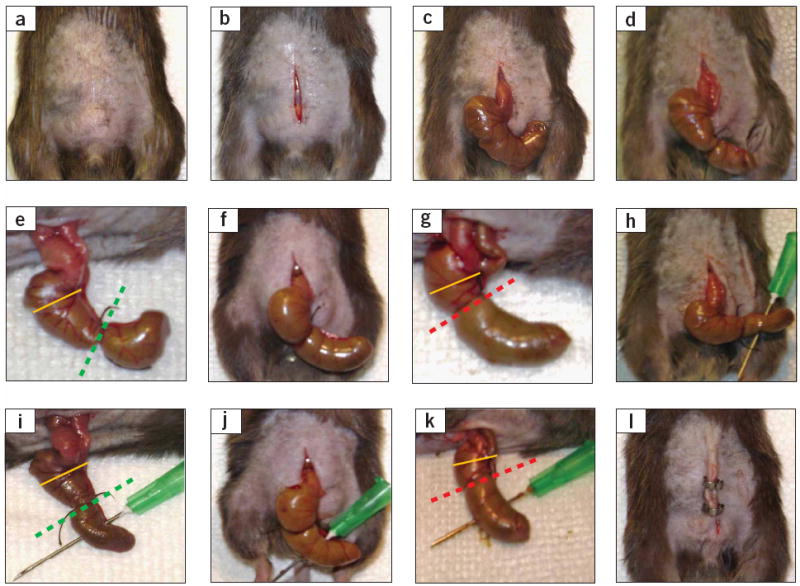
Critical steps in the CLP procedure in mice. (a) Disinfection of the abdominal area after shaving (Step 4). (b) Skin midline incision (Step 6). (c) Exposure of the cecum, which can be mostly found in the lower left area of the abdominal cavity (Step 8). (d,e) Ligation of the cecum at designated positions as the major determinant of sepsis severity (Step 10). For the induction of mid-grade sepsis resulting in survival rates of ~ 40%, the cecum is ligated (indicated by dotted green line) at half the distance between distal pole and the base of the cecum (black dotted line). (f,g) High-grade sepsis (100% lethality) comprises ligation of 75% of the cecum (dotted red line). The basis of the cecum is indicated by the yellow line. (h,i) Cecal puncture (‘through-and-through’) from mesenteric toward antimesenteric direction after medium ligation (Step 11). (j,k) Needle puncture of the cecum under the conditions of high-grade sepsis (large ligation; Step 11). (l) Wound closure by applying simple running sutures to the abdominal musculature and metallic clips to the skin (Steps 14 and 15).
