Figure 2.
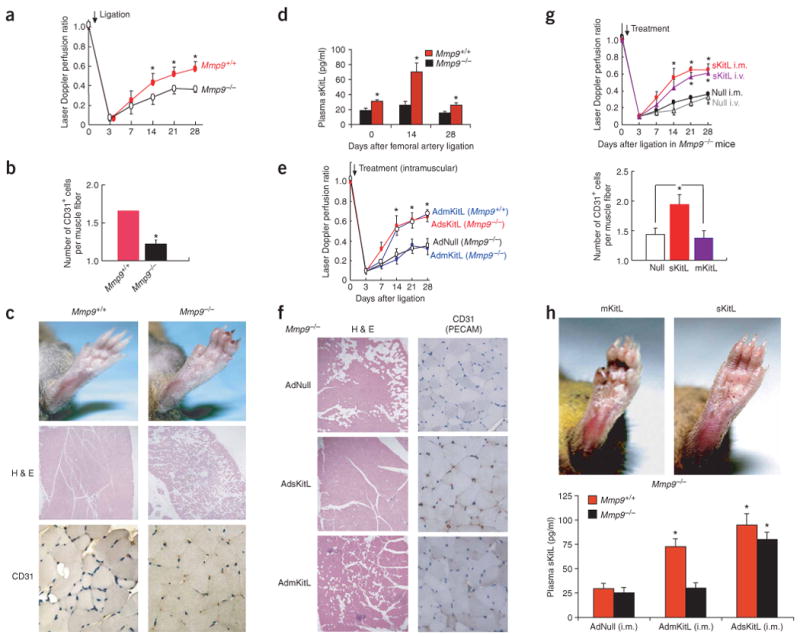
sKitL but not mKitL restores ischemic revascularization in angiogenesis-defective Mmp9−/− mice. (a) The Laser Doppler perfusion ratio was impaired in Mmp9−/− mice compared to Mmp9+/+ controls (n = 12 per group, *P < 0.05). (b) Vessel density (CD31+ cells/muscle fiber) decreased significantly in Mmp9−/− mice compared to Mmp9+/+ controls (n = 12 per group, *P < 0.005). (c) At 28 d after ligation, ischemic footpads showed profound swelling, ulceration and necrosis in Mmp9−/− compared to Mmp9+/+ mice (upper panels). H&E staining of Mmp9+/+ mice showed restoration of angiomyogenesis (middle panels; original magnification, ×100). Mmp9−/− mice showed loss of viable tissues followed by necrosis and adipose replacement. CD31 (PECAM-1) staining of hindlimb muscle sections showed decreased vessel density in Mmp9−/− mice (bottom panels; original magnification, ×400). (d) Hindlimb ischemia induced elevation of sKitL in plasma in Mmp9+/+ but not in Mmp9−/− (n = 6 per group, *P < 0.05). (e) Adenoviral delivery of mKitL (AdmKitL, single dose of 108 p.f.u.) augmented blood flow in Mmp9+/+ but not Mmp9−/− mice (n = 5 per group; P < 0.05). Adenoviral delivery of sKitL (AdsKitL, single dose of 108 p.f.u.) accelerated ischemic revascularization in Mmp9−/− mice. Control mice were injected with 108 p.f.u. of AdNull. (f) H&E (left panels; original magnification, ×100) and CD31 (right panels; original magnification, ×400) staining of lower limb tissue of Mmp9−/− mice injected with AdNull (upper panels), AdsKitL (middle panels) and AdmKitL (bottom panels) 28 d after ligation. Loss of viable tissues with adipose replacement and muscle necrosis was seen after treatment with AdNull or AdmKitL, but not in the AdsKitL-treated group, in which there was restoration of angiogenesis. (g) Intramuscular (i.m.) or intravenous (i.v.) delivery of AdsKitL (single dose of 108 p.f.u.) into Mmp9−/− mice accelerated revascularization comparably in ischemic hindlimbs (upper graph). Vessel density increased in AdsKitL-treated Mmp9−/− mice compared to AdNull- or AdmKitL-treated Mmp9−/− mice (lower graph) (n = 6 per group, *P < 0.05). (h) Reversal of ischemia-induced vasculopathy was observed in Mmp9−/− mice treated with sKitL, but not with mKitL (upper panels). Intramuscular AdmKitL (108 p.f.u.) injected into ischemic hindlimb increased sKitL plasma levels in Mmp9+/+ but not in Mmp9−/− mice 3 d after ligation (n = 4 per group, *P < 0.05). AdsKitL (108 p.f.u.) increased plasma sKitL threefold in Mmp9+/+ and Mmp9−/− mice compared to AdNull (n = 4 per group, *P < 0.05).
