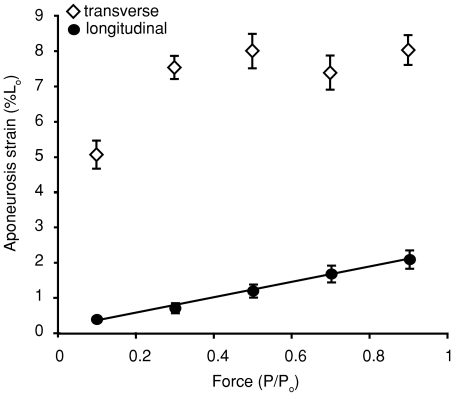
Figure 3. The relationship between active muscle force and peak aponeurosis strain during a muscle contraction.
Aponeurosis strain along the muscle's line of action (longitudinal) increases linearly with muscle force (P < 0.001). The data are fitted with a linear least-squares regression described by the equation y= 1.9x+ 0.17. Aponeurosis strain orthogonal to the muscle's line of action (transverse) increases with force across contractions at relatively low forces but reaches a plateau across the higher range of forces. Note that transverse strain is on average about four times greater than longitudinal. Data shown are pooled from four individuals. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Positive strain values represent tissue extension. Muscle force is plotted as the proportion of the maximum isometric force (Po).