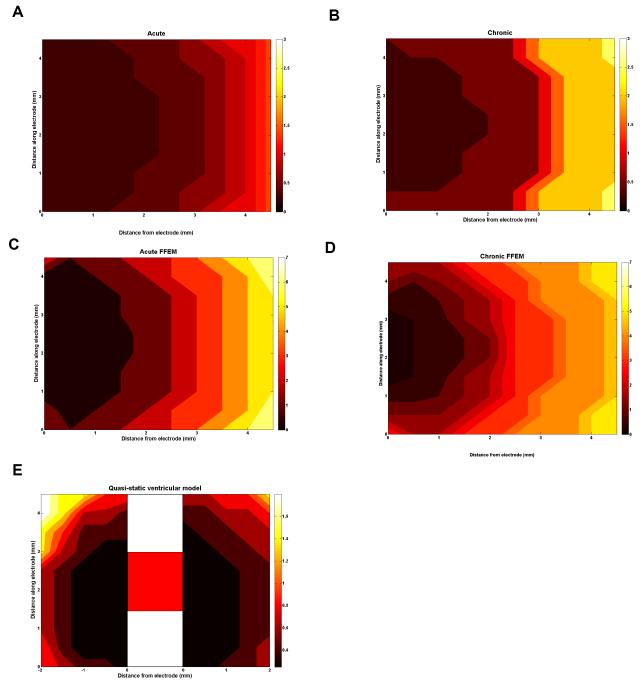
Figure 5.
These plots show the potential amplitude required in monopolar stimulation to stimulate axons in the surrounding tissue. For each axon location, the potential threshold is plotted for each model presented: the quasi-static model acute (A) and chronic (B), FFEM acute (C) and chronic (D), and the anatomical model of the peri-ventricular gray (E). In all cases the axons are orientated perpendicular to the electrode. As the first 4 models predict a symmetric electric field, the axons are only located to one side of the electrode, as shown in figure 2B. In the ventricle case (E), the field is not symmetric and therefore, the axons are located either side of the electrode (shown schematically in the centre) for comparison, as the left hand side of the VTA is the ventricle side and the right hand side is the opposite side of the electrode. The potential thresholds rely greatly on the state of the EBI, as well as the surrounding anatomical details.