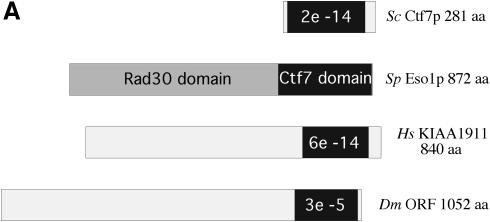
Figure 1.
Identification of Ctf7p-like proteins in higher eukaryotes. (A) Schematic illustrating Eso1p and conceptual translations of cDNAs that encode Ctf7p-like proteins. E values (a measurement of similarity) for Ctf7p domains are shown in black. The N-terminal region of Eso1p that exhibits homology to Rad30p is shown in dark gray. Regions that extend upstream of the Ctf7p region in human and Drosophila are shown in light gray. (B) Amino acid alignments reveal the high degree of conservation of the Ctf7p domain for a selection of coding sequences. Residues are numbered according to conceptual translations of cDNA sequences, except for contig sequences which were assigned a starting residue number of 1. Accession numbers are as follows: Schizosaccharomyces pombe Eso1p (BAA95122), Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ctf7p/Eco1p (NP 116683), Drosophila melanogaster (AAF50579.1), Mus musculus ORF (MGC:30637), Homo sapiens KIAA1191 (AB067498) and Homo sapiens contig (comprised of N94144, BG288675 and BE247544). Other mouse (AAH08220, BAB26905 and AA881675) and human orthologs were also identified.