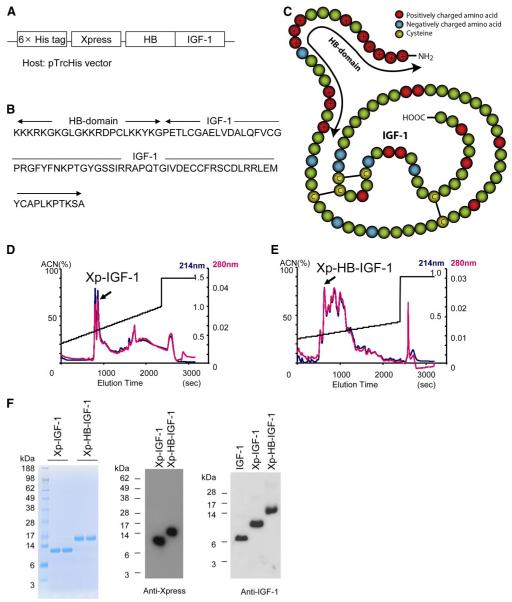
Figure 1.
Construction and purification of a new Xp-HB-IGF-1 fusion protein. A) The heparin binding domain of HB-EGF was inserted N-terminal to IGF-1 to generate the fusion protein. The construct included the hexahistidine and Xpress tags from the pTrcHis vector for purification and detection. B) The resulting amino acid sequence of HB-IGF-1. C) Schematic for the structure of HB-IGF-1. Red circles: positively charged amino acids; blue circles: negatively charged amino acids; yellow circles: cysteines. The arrow shows the HB domain. In this figure the epitope tags are not shown. D, E) Representative reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) elution profiles with single peaks containing correctly folded protein. Readings of optical density at 214 nm are in blue; readings at 280 nm are in red; elution is by acetonitrile (ACN) gradient. F) After RP-HPLC, Coomassie blue staining and Western blot analysis demonstrate isolation of single bands containing Xpress-tagged protein. The right panel shows that the Western blot analysis of IGF-1, and the two engineered IGF-1 proteins yield similar results using an anti-IGF-1 antibody.