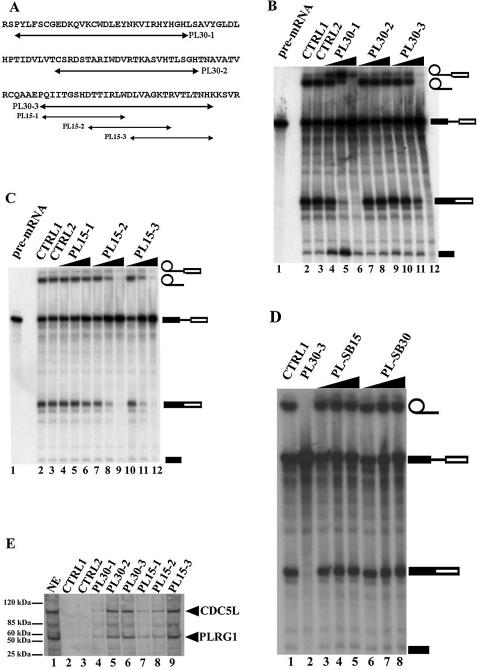
Figure 2.
PLRG1 peptides will interact with CDC5L in nuclear extract and inhibit pre-mRNA splicing. (A) Design of peptides from sequences in the CDC5L binding region of PLRG1. The arrows indicate the sequences of the peptides synthesised. (B) Autoradiograph of a splicing gel from an experiment to determine the effect of 24mer–30mer peptides spanning the highly conserved WD40 sequences on splicing. Approximately 7–20 nmol peptide were added to the splicing reactions (lanes 4–12). Lane 1 contained the input pre-mRNA. CTRL1 is a control splicing reaction without peptide. CTRL2 is a control reaction containing 20 nmol control peptide HC-2 derived from another spliceosomal protein HCF-1 that has not been detected in complexes containing CDC5L and PLRG1. The symbols on the right of the panel represent the input RNA, splicing intermediates and products. (C) Autoradiograph of a splicing gel from an experiment to determine the effect of overlapping 15mer peptides spanning the PL30-3 sequence on splicing. Similar amounts of peptide were added (lanes 4–12) to the splicing reactions as in (B). The lanes marked CTRL1 and CTRL2 contained splicing reactions treated in a similar way to lanes with the same names in (B). (D) Peptides containing the same amino acids as PL15-3 and PL30-3 in a scrambled sequence do not inhibit splicing. Lane 1, CTRL1 is the control reaction without peptide; lane 2, ∼20 nmol PL30-3; lanes 3–5, 7–20 nmol PL-SB15; lanes 6–8, 7–20 nmol PL-SB30 peptide. (E) Pull-down of CDC5L onto streptavidin–agarose beads from HeLa nuclear extract using PLRG1 peptides. Lanes 4–9, pull-down assays with the corresponding peptides (used in marking each lane). CTRL1 did not contain any peptides whereas CTRL2 contained a control peptide that does not inhibit splicing. The blot was probed with a buffer containing both anti-CDC5L and anti-PLRG1 antibodies. The arrows on the right of the panel show the positions of the CDC5L and PLRG1 proteins.