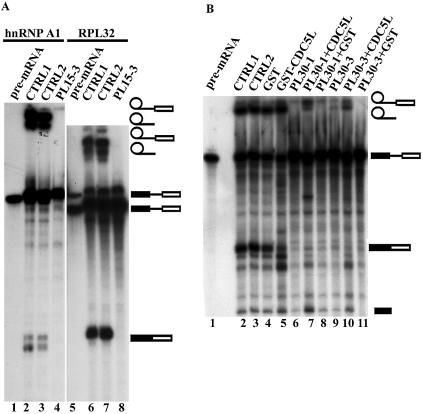
Figure 3.
(A) Effect of the PLRG1 inhibitory peptide on splicing using other pre-mRNA templates (hnRNP A1 and RPL32). Lanes 1 and 5 contain the input pre-mRNA. All the lanes marked CTRL1 are splicing controls without peptide. The lanes marked CTRL2 contained the control peptide PL-SB15. Lanes 4 and 8 are splicing reactions containing the PLRG1 inhibitory peptide PL15-3. (B) Bacterially expressed CDC5L reduces the effect of PLRG1 peptides in splicing inhibition. Splicing assays were performed using peptides that had been preincubated with either GST–CDC5L (∼40 µg) or a similar molar amount of GST for 15 min at room temperature. Lane 1, input pre-mRNA; lane 2 (CTRL1), a control splicing reaction without peptide; lane 3 (CTRL2), a negative control splicing reaction containing PL30-2; lanes 4 and 5, splicing reactions without peptides but to which had been added GST and GST–CDC5L, respectively, at the same levels as the protein used in preincubation with peptides; lane 6, splicing reaction containing peptide without recombinant protein. The reactions in lanes 7 and 8 are similar to that in lane 6 except that the peptides were preincubated with GST–CDC5L and GST, respectively. The splicing reactions in lanes 9–11 are identical except that the reaction in lane 9 contained PL30-3 peptide alone whereas the reactions in lanes 10 and 11 contained peptides preincubated with GST–CDC5L and GST, respectively. The symbols on the right of the panel represent the input RNA, splicing intermediates and products. Other bands in the figure have been caused by partial degradation of the RNA in the reactions.