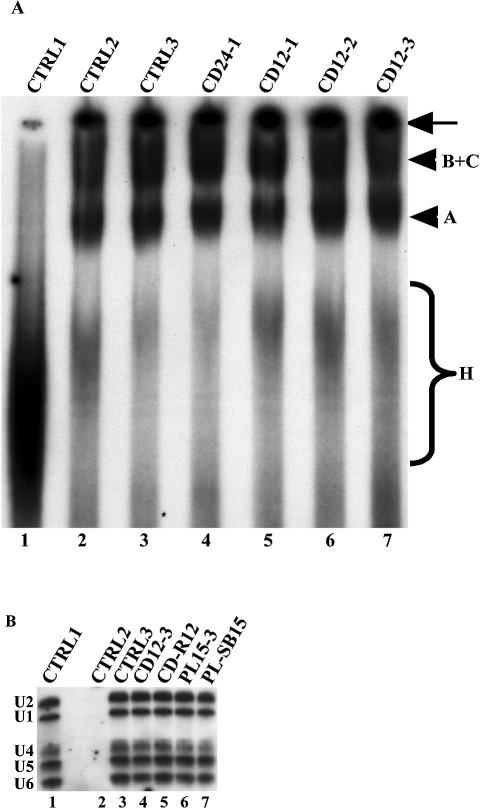
Figure 8.
Characterisation of splicing complexes formed in the presence of inhibitory peptides. (A) Splicing complexes are formed in the presence of CDC5L peptides that inhibit catalysis. CDC5L peptides were added to splicing reactions as described previously and the splicing complexes formed were separated on a polyacrylamide/agarose native gel. The bands representing splicing complexes were revealed by autoradiography. Lane 1, a control splicing reaction incubated on ice; lane 2 (CTRL2), a control splicing reaction without peptide; lane 3, a negative control containing the CD-R24 peptide that does not inhibit splicing; lanes 4–7, the CD24-1, CD12-1, CD12-2 and CD12-3 peptides, respectively. The arrow on the right indicates material that did not penetrate into the gel. The arrowheads represent the splicing complexes separated on the native gel. The brace labeled H indicates non-specific complexes assembled on the pre-mRNA. (B) Identification of snRNAs in splicing complexes formed in the presence of inhibitory peptides. Splicing complexes were formed (as above) using biotinylated pre-mRNA and as described in Materials and Methods. snRNAs in streptavidin–agarose pull-downs were analysed by northern blotting (26). The lane marked CTRL1 is the positive control showing all five snRNAs in HeLa nuclear extracts. CTRL2 contained a splicing reaction assembled on ice. CTRL3 contained a splicing reaction without peptide. The reaction in lane 4 contained the inhibitory CDC5L peptide CD12-3 and lane 5 contained the control CDC5L peptide that does not block splicing. The splicing reaction in lane 6 contained the inhibitory PLRG1 peptide, whereas the reaction in lane 7 contained the control PLRG1 peptide that does not inhibit splicing.