Fig. 5.
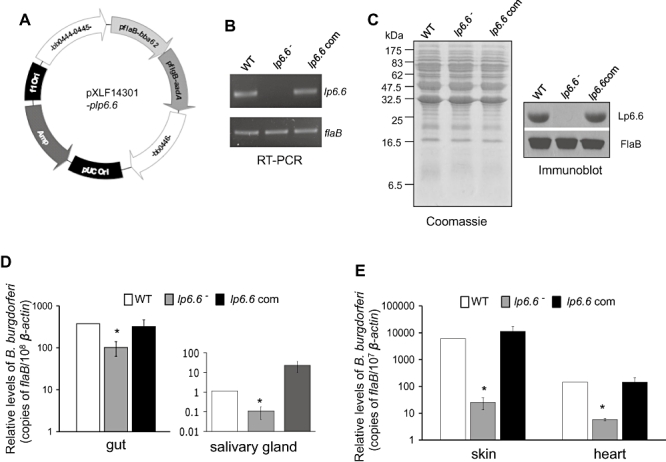
Complementation of lp6.6 mutant B. burgdorferi with lp6.6 restores the phenotypic defects of the mutant to transmit from ticks to mice. A. Construction of plasmid DNA pXLF14301-plp6.6 for cis-integration of the lp6.6 gene. The open reading frame of lp6.6 gene was fused with the flaB promoter and cloned into the shuttle vector pKFSS1 that houses the streptomycin resistance gene (aadA) under B. burgdorferi flgB promoter. The flaB promoter–lp6.6 gene fusion and aadA cassette was finally cloned into pXLF14301, which contains DNA fragments for homologous recombination and integration of the complemented gene in the B. burgdorferi genome. B. RT-PCR analysis of the lp6.6 transcripts. Total RNA was isolated from either the wild-type (WT), lp6.6 mutant (lp6.6−) or lp6.6-complemented B. burgdorferi (lp6.6 com), converted to cDNA, then subjected to PCR analysis with flaB and lp6.6 primers, and analysed on an agarose gel. C. Restoration of Lp6.6 protein by the complemented B. burgdorferi. Lysates of B. burgdorferi were separated on a SDS-PAGE gel, which was either stained with Coomassie blue or transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with antiserum against Lp6.6 or FlaB. D. B. burgdorferi transmission through infected ticks. B. burgdorferi-infected nymphs were generated by feeding larvae on mice infected with wild-type and genetically manipulated B. burgdorferi (two mice per group) as described in the text. Newly molted B. burgdorferi-infected nymphs were allowed to feed on naïve mice (five ticks per mouse, five animals per group). B. burgdorferi burdens were assessed in dissected tick guts (left) or salivary glands (right) at 2 days of feeding by measuring copies of the B. burgdorferi flaB RNA and normalized against tick β-actin RNA levels. E. B. burgdorferi transmission from infected ticks to mice. B. burgdorferi-infected nymphs were fed on mice as described in (D) and spirochete levels were assessed in the indicated murine tissues at 7 days of tick feeding. The bars represent the mean values and the error bars represent the SEM values from two independent animal infection experiments. Burdens of wild type and lp6.6-complemented mutants are significantly higher than corresponding levels of lp6.6 mutants (*P < 0.05).
