FIG. 1. The ccz1Δ and mon1Δ strains are defective in the Cvt, autophagy, and pexophagy pathways.
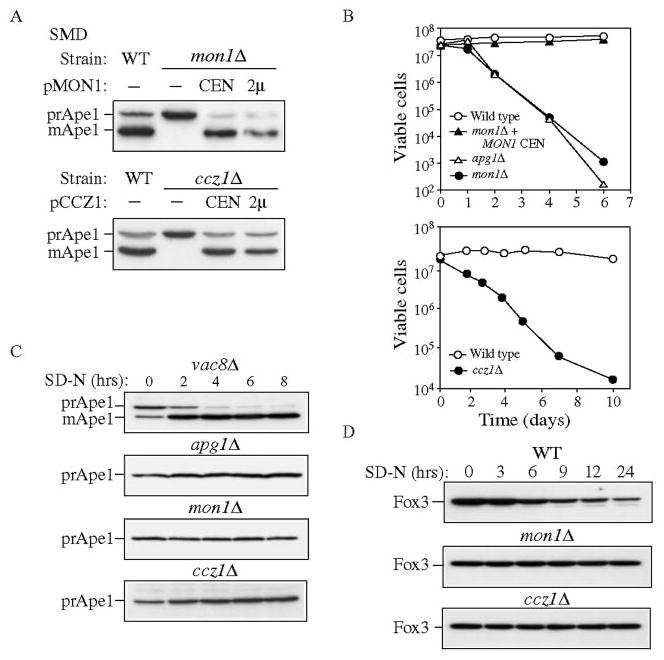
A, cloning and characterization of CCZ1 and MON1. Wild type (WT, SEY6210), ccz1Δ (CWY3), and mon1Δ (JSY1) strains and the knockout strains expressing the respective single copy (CEN) or multicopy (2μ) plasmids were grown in SMD medium and analyzed by immunoblot against Ape1. B, mon1Δ and ccz1Δ strain are sensitive to nitrogen-starvation conditions. The wild type, apg1Δ, and mon1Δ strains and the mon1Δ strain harboring pMON1(416) or the wild type and ccz1Δ strains were grown to mid-log phase in SMD medium and shifted to SD-N medium. At the indicated time, aliquots were removed and spread onto YPD plates in triplicate. The number of viable colonies was counted after 2 days incubation at 30 °C. C, mon1Δ and ccz1Δ mutants do not bypass the prApe1 accumulation defect when autophagy is induced. The vac8Δ (D3Y102), apg1Δ (NNY20), ccz1Δ, and mon1Δ strains were grown to mid-log phase in SMD and shifted to SD-N medium. At the indicated time, aliquots were removed and subjected to immunoblot against Ape1. D, mon1Δ and ccz1Δ strains are defective for pexophagy. The wild type, ccz1Δ and mon1Δ strains in the BY4742 background were grown in YPD to mid-log phase, transferred to oleic acid medium to induce peroxisome production and shifted to SD-N. Aliquots were removed at the indicated times and analyzed by Western blot with antiserum to Fox3.
