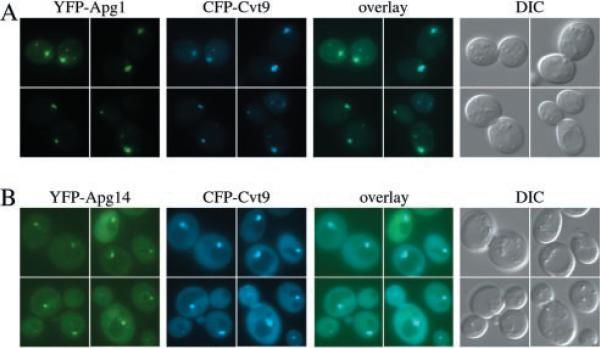
Fig. 2. The Apg1 protein kinase and the Apg14 component of the PI 3-kinase co-localize with Cvt9.
Wild type cells (SEY6210) were co-transformed with plasmids, under CUP1 copper-inducible control, expressing either YFP-Apg1 (pCuYFPAPG1(426)) and CFP-Cvt9 (pCuCFPCVT9(424)) (A) or YFP-Apg14 (pCuYFPAPG14(426)) and CFP-Cvt9 (B). Transformed cells were grown to midlog stage in SMD, induced for 1–2 h with 30 μm CuSO4, and viewed directly (B) or shifted to SD-N medium for 1 h prior to microscopy analysis (A). Images were captured and analyzed as in Fig. 1. The YFP fusion of the Apg1 kinase, and Apg14, a subunit of the Apg/Cvt-specific Vps15/34 PI-3 kinase complex, co-localize with the perivacuolar CFP-Cvt9 fusion protein. DIC, differential interference contrast.