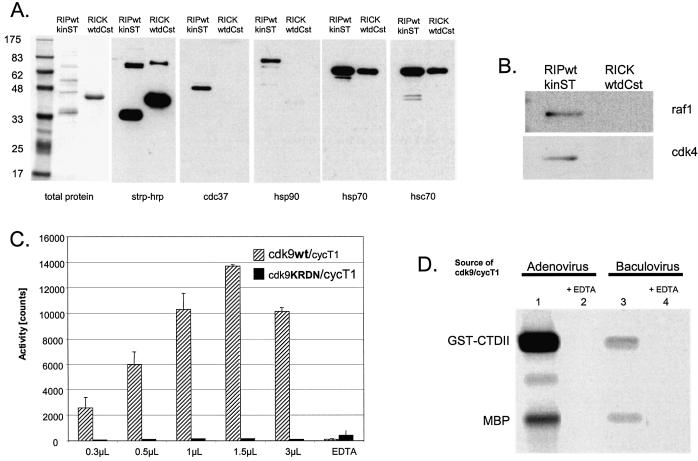
Figure 4.
(A and B) Copurifying proteins. RICKdC and RIPkin (both as wild type kinase) were expressed in 293 cells, extracted and purified by streptavidin–Sepharose. Similar quantities of each protein were resolved by SDS–PAGE and stained for total protein (left side) or transferred to nitrocellulose, stained with either streptavidin-HRP or the indicated antisera followed by HRP-conjugated secondary antibody and then by ECL. (C) cdk9/cycT1 wt versus KRDN activity. Equal quantities of cdk9/cycT1 (wt or KRDN) were incubated under cdk9 kinase conditions in the presence of [γ-33P]ATP and an RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal peptide as a substrate (see Materials and Methods). (D) Comparison of adenovirus and baculovirus-produced cdk9/cyclinT1. For baculovirus production, Sf9 cells were infected with baculoviruses directing the expression of His-tagged cdk9 and cyclin T1. Purification was performed essentially as described (30). Equal quantities of purified protein derived from adenovirus (lanes 1 and 2, see Materials and Methods) or baculovirus (lanes 3 and 4) were tested in the absence of EDTA (lanes 1 and 3) or presence of 10 mM EDTA (lanes 2 and 4) for their ability to phosphorylate GST-CTDII plus MBP as described in Materials and Methods.