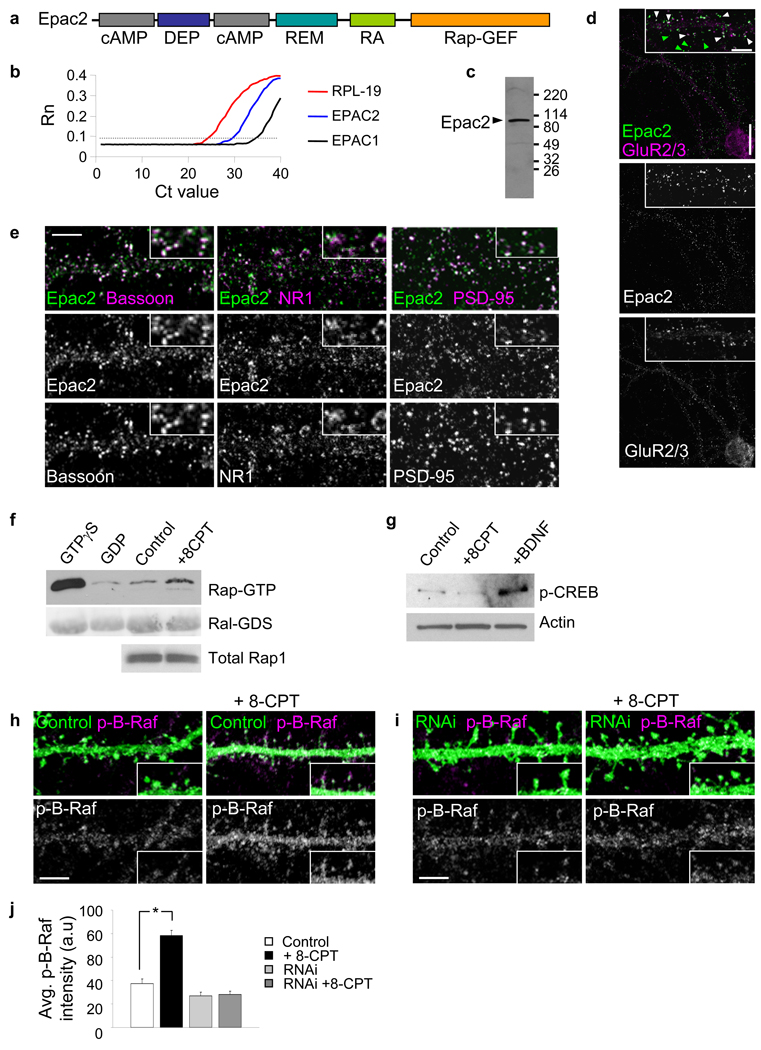
Figure 1.
Epac2 is present in synapses in cultured cortical pyramidal neurons. (a) Domain structure of Epac2. (b) Quantitative PCR analysis of Epac1 and Epac2 mRNA in cortical neurons (div 28) demonstrates the relative enrichment of Epac2. (c) Western blot detection of Epac2 in rat forebrain homogenate. (d) Localization of Epac2 in cultured cortical pyramidal neurons (div 28); colocalization with GluR2/3. White arrowheads, colocalization; green arrowheads, non-colocalized Epac2 puncta. (e) Double immunofluorescence with antibodies for synaptic proteins bassoon, NR1 and PSD-95. (f) Epac2 activation by 8-CPT (50 µM, 1 hr) in cortical neurons; endogenous Rap activation was measured. Fold Rap activation compared to control: 1.57±0.11 fold increase, *P<0.001, n = 4. (g) Specificity of 8-CPT for Epac2 in neurons: effect of 8-CPT or BDNF on CREB phosphorylation, n = 3 (h) Effect of incubation with 8-CPT (50 µM, 1 hr) on the phosphorylation of the Rap target B-Raf in situ in pyramidal neuronal dendrites. (i) Effect of incubation with 8-CPT (50 µM, 1 hr) on B-Raf phosphorylation in dendrites of neurons expressing Epac2 RNAi. (j) Quantification of B-Raf fluorescence intensities in h-i (*P<0.001), n = 9–12 cells per condition, 3 experiments. Error bars: s.e.m. Scale bars: d, 15 µm; d-zoom, e, h, i, 5 µm.